Join Our Telegram channel to stay up to date on breaking news coverage
Decentralization is a cornerstone of the blockchain philosophy, and Ethereum developers are currently giving high priority to a new design element that can further the idea. The concept of “Distributed Validator Technology” or DVT is being promoted for this cause.
What is Distributed Validator Technology?
According to BeaconScan, the Ethereum blockchain relies on 606,947 validators to validate network transactions, yet each one of them might be viewed as a potential weak point. To boost validator resilience and decrease single points of failure, distributed validator technology distributes key management and signature tasks among several parties.
By decreasing single points of failure, the objective is to strengthen the network’s resilience while also safeguarding the individual validators.
The validators themselves may also be subject to harsh financial penalties known as “slashing” if they go down for an extended period. The validators are therefore motivated to become more resilient themselves.
How does DVT Work?
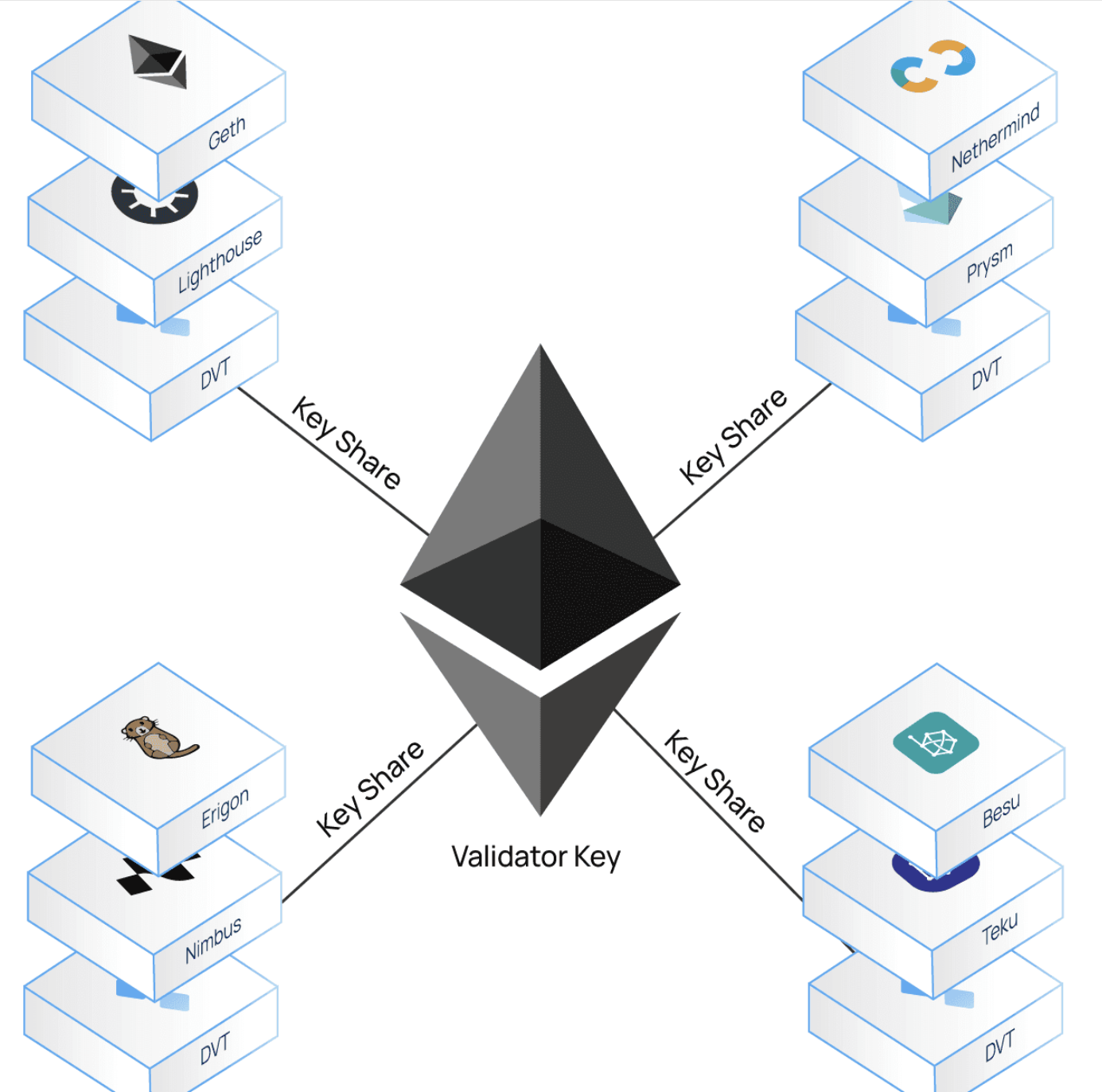
Distributed Validator Technology works by distributing the private key needed to protect a validator across a large group of machines known as a “cluster”. The advantage of this is that because the key is not entirely stored on one system, it becomes more difficult for attackers to access the key. As only a portion of the computers in each cluster can do the required signature, it also enables certain nodes to go offline.
As a result, the network’s single points of failure are decreased, and the entire validator set becomes more reliable. The concept is to allow for the decentralization of the validators themselves.
Twitter user Collin Myers told the community about this technology about two years ago.
Distributed Validator Technology (or DVT, for short), is a new infrastructure primitive that enables a validator key to be split between independently operating validator instances, enabling Active Active redundancy across Eth2 infrastructure deployments. pic.twitter.com/q69TJnlNsN
— Collin Myers (@StakeETH) December 2, 2021
Why the Hype Around the Concept?
The ideal situation for Ethereum is to have as many validators that are run independently as possible. However, a small number of staking companies have grown to be highly well-liked and represent a sizeable fraction of the overall amount of ETH staked on the network.
These operators may continue to operate with the decentralization of stake protected thanks to DVT. This is because each validator’s keys are spread across numerous machines, making it considerably more difficult for a validator to turn malevolent.
The DVT Concept
DVT offers an array of benefits to Ethereum, including decentralization of Ethereum’s proof-of-stake consensus and ensuring that the network is active and validator fault tolerance is created. At the same time, it reduces the chances of slicing and downtime while enhancing diversity in terms of clients, data centers, locations, and rules.
Without DVT, staking providers would find it simpler just to support one or two client configurations for all their validators, which would increase the impact of a client problem. By dispersing the risk among several client setups and hardware, DVT can build resilience through diversity.
Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has placed distributed validators among the blockchain’s main priorities since at least 2021. This was when he wished the Beacon Chain a happy birthday and offered an updated plan for the second-largest blockchain by market capitalization, known for its smart contracts.
In recent months, DVT has drawn increased attention from developers and entrepreneurs at companies including Messari, Coin Metrics, Bankless, Wu Blockchain, and Pantera Capital as well.
Roadmap Ahead
DVT also has substantial effects on the broader staking market, including permissionless operator participation, non-custodial staking, staking as a service, staking pools, and liquid staking providers.
As Obol and SSV prepare to introduce distributed validators to the Ethereum mainnet, they represent the final significant advancement in Ethereum’s Merge era prior to “The Surge.”
With the launch of its public testnet, Jato, in March, SSV is in the final phase before launching its mainnet, and Obol began deploying distributed validators on the Ethereum mainnet in April.
DVT “makes the heart of the crypto universe – Ethereum – more robust, more decentralized and credibly neutral, opening its protocols and uses to all in a more stable manner,” according to Smith.
Related News
Best Wallet - Diversify Your Crypto Portfolio
- Easy to Use, Feature-Driven Crypto Wallet
- Get Early Access to Upcoming Token ICOs
- Multi-Chain, Multi-Wallet, Non-Custodial
- Now On App Store, Google Play
- Stake To Earn Native Token $BEST
- 250,000+ Monthly Active Users
Join Our Telegram channel to stay up to date on breaking news coverage