Whether you’re paying someone, moving cash from one wallet to another, or getting cryptocurrency from an exchange or a friend, knowing how to send and receive Bitcoin securely is important. It’s simple, but there are things you don’t want to forget, especially when real money is involved.
In this article, we’ll cover what you’ll need, walk you through sending and receiving, and point out some typical mistakes to steer clear of. Before you know it, you’ll be purchasing and selling Bitcoin like a pro.
Key Takeaways
- Choose a trusted wallet (hardware is safest), keep your private keys/seed phrase offline, and back them up safely.
- Double-check recipient addresses (especially if copied), use QR codes when possible, and watch out for address-changing malware.
- Set appropriate fees for timely processing, wait for confirmations, and beware of scams. Bitcoin transactions are final and irreversible.
What You Need to Send and Receive Bitcoin
There are a couple of things you need if you wish to send and receive Bitcoin with ease, including a wallet, a Bitcoin address, and sufficient money to cover fees. Let’s break them down.
1. A Bitcoin Wallet
You need to have a crypto wallet to send or receive Bitcoin. Consider it as your own virtual bank account that stores your BTC and enables you to interact with the blockchain
There are a few types of wallets:
- Software wallets (like Electrum or Exodus) run on your desktop.
- Mobile wallets (like Trust Wallet or BlueWallet) work through smartphone apps.
- Hardware wallets (like Ledger or Trezor) are physical devices that store your keys offline for extra security.
- Web wallets are browser-based and usually tied to exchanges like Coinbase or Binance.
To obtain one, download an app for a wallet or purchase a hardware wallet, set it up according to the instructions, and store your recovery phrase somewhere safe. That’s the only way that you can recover your wallet if you lose access to it.
2. A Bitcoin Address
A Bitcoin address is what you give to someone who wants to send you BTC. It is a long, unique string that looks like this:
bc1qxy2kgdygjrsqtzq2n0yrf2493p83kkfjhx0wlh
You’ll find your address inside your wallet. Most wallets generate a fresh one for every transaction to keep things private. You can copy it manually or just scan a QR code if you’re in person. Never try to type it out by hand, it’s too easy to mess up.
3. Network Fees
Every time you send Bitcoin, you’ll have to pay a small transaction fee. These fees go to the miners who process transactions and secure the network.
The fee amount depends on network traffic and how fast you want the transaction to go through. Most wallets let you choose between low fees for slower confirmations or medium/high fees if you want it confirmed fast.
Some wallets offer fee estimators or auto-adjust fees for you. Either way, double-check before sending because underpaying can delay your transaction, but overpaying isn’t ideal either.
How to Send Bitcoin
Once your wallet is set up and you’ve got some BTC, sending it is a very easy step-by-step process. Here’s how it works.
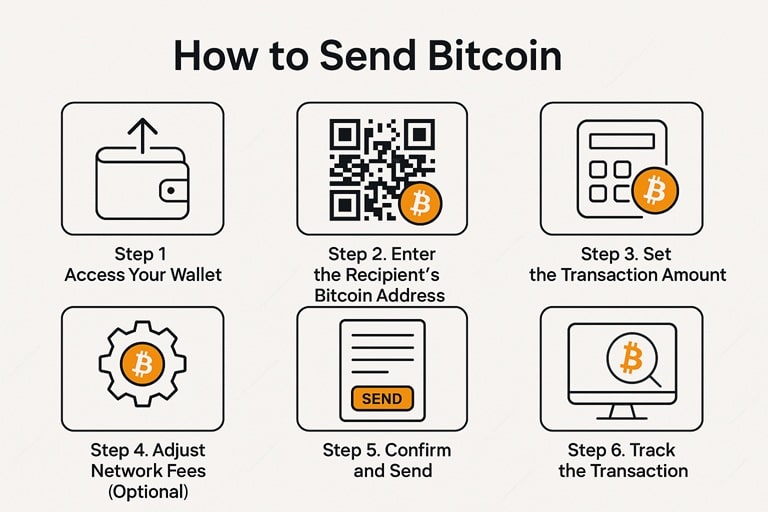
Step 1: Access Your Wallet
Open your wallet app or log in through your browser. Make sure your balance covers both the amount you want to send and the network fee. If you’re using a hardware wallet, you’ll also need to connect it.
Step 2: Enter the Recipient’s Bitcoin Address
You can either paste their Bitcoin address or scan a QR code if they’ve provided one. Always double-check the address because once you send BTC, there’s no way to go back.
Step 3: Set the Transaction Amount
You can usually choose to send a specific amount in BTC or its equivalent in fiat (like USD or EUR). Some wallets also have minimum or maximum limits, especially if you’re using an exchange wallet, so keep an eye on that.
Step 4: Adjust Network Fees (Optional)
Your wallet might give you options like “slow,” “normal,” or “fast” transaction speeds. Higher fees usually mean faster confirmations. Use built-in fee estimators or sites like mempool.space to get a real-time idea of what fee makes sense.
Step 5: Confirm and Send
Before hitting send, double-check everything: the address, the amount, and the fee. Some wallets may also ask for two-factor authentication or a hardware wallet confirmation. Once confirmed, your transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network.
Step 6: Track the Transaction
You can use a blockchain explorer (like blockstream.info or btcscan.org) to follow your transaction in real-time. It’ll show how many confirmations it has and whether it’s complete. Most services require 1–3 confirmations for the funds to be considered final.
How to Receive Bitcoin
Receiving Bitcoin is even easier than sending it. Still, you’ll want to do it the right way to keep your funds safe and make sure everything goes smoothly.
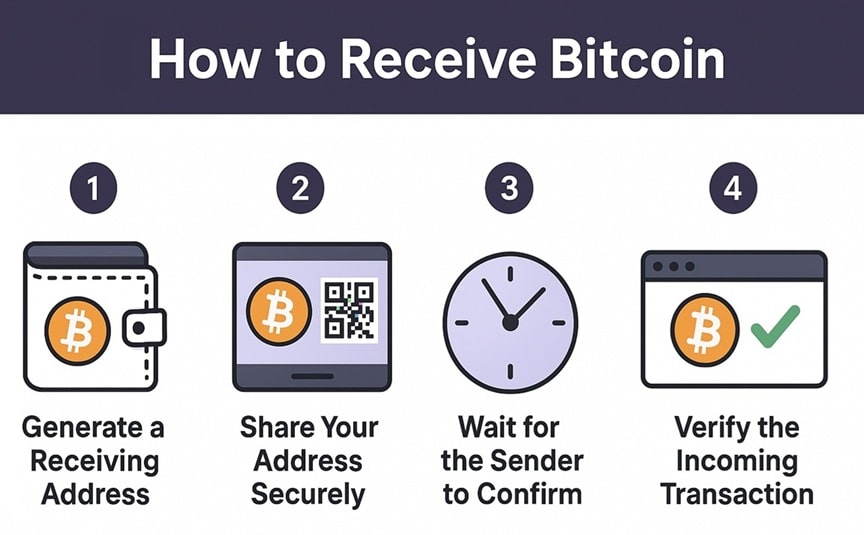
Step 1: Generate a Receiving Address
Open your wallet and tap on “Receive” or “Request.” It’ll generate a Bitcoin address for you. It’s usually in the form of a long string like we’ve seen before and a QR code. Some wallets recommend creating a new address for each transaction to protect your privacy, while others let you reuse the same one.
Step 2: Share Your Address Securely
You can share your Bitcoin address by sending the text version or the QR code. If you’re texting or emailing it, double-check for typos or weird formatting.
Also, you should never share your private key—only the public address. Beware of fake apps or phishing links. If someone sends you an address that looks slightly off, it might be a scam.
Step 3: Wait for the Sender to Confirm
Once the sender initiates the transfer, ask them to confirm that it’s been sent. They might also share the transaction ID (TXID), which you can use to track it on a blockchain explorer.
Step 4: Verify the Incoming Transaction
Your wallet will show when the transaction is received and how many confirmations it has. One confirmation is often enough for smaller payments, but bigger transfers might require three or more. Once it’s confirmed, your BTC balance will update.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
When things go wrong, it’s better to know what’s happening and what to do. Here are some common issues with sending and receiving Bitcoin, and how to deal with them.
Transaction Delays
If your BTC transfer is taking longer than expected, it’s usually because the network is congested or the fee is too low. You can:
- Use a blockchain explorer to check how many unconfirmed transactions are ahead of yours.
- Try fee bumping (if your wallet supports it) or use Replace-by-Fee (RBF) to speed it up.
- Wait it out. Most stuck transactions clear within a few hours or days.
Wrong Address Sent
Unfortunately, Bitcoin transactions can’t be reversed. If you sent BTC to the wrong address:
- Double-check the transaction ID to confirm where it went.
- If you know the person who controls the address, ask them to return it.
- If it’s a scam or mistake, there’s no real way to get it back.
Always triple (even quadruple)-check the recipient’s address before hitting send, and send a small test transaction ahead of the major transfer to ensure it works perfectly. A single wrong character can cost you everything.
Low or Missing Funds After Receiving
If you received less BTC than expected, it’s probably due to network fees charged by the sender’s wallet or the exchange they used. It can also happen if your wallet isn’t fully synced.
Try:
- Refreshing your wallet or restarting the app.
- Waiting for more confirmations.
- Checking if the incoming amount matches the blockchain record.
Sending and Receiving Bitcoin FAQs
How long does it take to send Bitcoin?
It usually takes 10 to 60 minutes, depending on the network fee and congestion. Low-fee transactions can take hours.
What happens if I send Bitcoin to the wrong address?
It’s gone. Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. Always double-check the address before confirming.
Can I cancel a Bitcoin transaction?
No. Once it’s broadcast to the network, it’s out of your hands. Some wallets offer Replace-by-Fee (RBF), but that only works under certain conditions and must be enabled before sending.
Why is my Bitcoin transaction taking so long?
Probably because of a low fee or high network traffic. You can track it using a blockchain explorer to see how many confirmations it has.
How do I check if my Bitcoin transaction was successful?
Paste the transaction ID (TXID) into a site like blockstream.info. It’ll show the status and confirmations.
Do I need to pay a fee when receiving Bitcoin?
No, the sender pays the network fee. You receive the full amount (minus any deductions made on their end).
What is the safest way to share my Bitcoin address?
Either copy-paste it or use a QR code. Never type it out manually. And never share your private key—just the public address.
How do I increase the speed of my Bitcoin transaction?
Use a higher network fee. You can also try RBF or a fee bump if your wallet supports it.
Are Bitcoin transactions reversible?
No. Once confirmed, they’re final. That’s why triple-checking everything is key.
Can I send Bitcoin without an internet connection?
Not directly. You need an internet connection to broadcast the transaction. Some apps let you prepare it offline and send it later—but it still needs to go online at some point.
References
- Getting Started with Bitcoin – Bitcoin.org
- How to Send and Receive Bitcoin – Ledger Academy
- What is RBF (Replace-By-Fee)? – Bitpay