Buying cryptocurrency can seem overwhelming at first, filled with unfamiliar terminology, various purchasing platforms, and important security considerations. But buying Bitcoin doesn’t have to be complicated. This step-by-step guide breaks down everything from choosing the right exchange and payment method to securing your digital assets for the long term.
By the time you finish reading, you’ll understand the methods of buying Bitcoin and also the crucial security practices that will help protect your investment.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin can be purchased through various platforms, including exchanges, P2P platforms, and Bitcoin ATMs. Each option offers different tradeoffs between convenience, security, fees, and privacy.
- Using hardware wallets for large amounts, enabling 2FA, and securely storing your recovery phrase offline can protect your investment from hacks and theft.
- Different buying strategies exist based on your goals, from dollar-cost averaging for gradual investment to long-term “HODLing.”
Why Buy Bitcoin?

Before exploring how to buy Bitcoin, it’s worth understanding why many people choose to invest in this digital asset in the first place.
Bitcoin has shown remarkable long-term growth despite its volatility. From January 2024 to January 2025, Bitcoin’s price increased from approximately $43,000 to an all-time high of almost $109,000—a growth of over 150%. However, this comes with significant risk, as Bitcoin has historically experienced dramatic price drops of 65-80% during bear markets.
Another reason why people buy BTC is its fixed supply limit of 21 million coins. Unlike government-issued currencies that can be printed infinitely, Bitcoin’s scarcity is programmed into its code. This built-in scarcity is why many investors see it as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
Another reason can be portfolio diversification. Financial advisors often recommend diversifying investments across different asset classes. Despite its volatility, Bitcoin’s price movements often don’t correlate directly with stocks, bonds, or real estate, potentially making it a useful diversification tool.
Use Cases Beyond Investment
Obviously, Bitcoin isn’t just a speculative asset. It has many practical purposes, and its adoption grows day by day. Here are other reasons why people choose to buy BTC:
- To send money across borders without traditional banking limitations
- Some investors see Bitcoin as “digital gold” due to its fixed supply cap of 21 million coins
- Provides banking-like services to the unbanked population worldwide
- Enables potentially cheaper international money transfers
Risks and Volatility Considerations
Bitcoin’s price can swing dramatically—sometimes 5-10% in a single day. This volatility makes it unsuitable for funds you might need in the short term. As a rule of thumb, never invest more in Bitcoin than you can afford to lose.
Before You Buy Bitcoin
Before making a purchase, you need to understand how Bitcoin wallets work and where you’ll store your investment. Unlike traditional currencies that you can hold physically or keep in a bank account, Bitcoin exists entirely on the blockchain. Think of it like a digital keychain rather than a traditional wallet that holds physical currency.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets
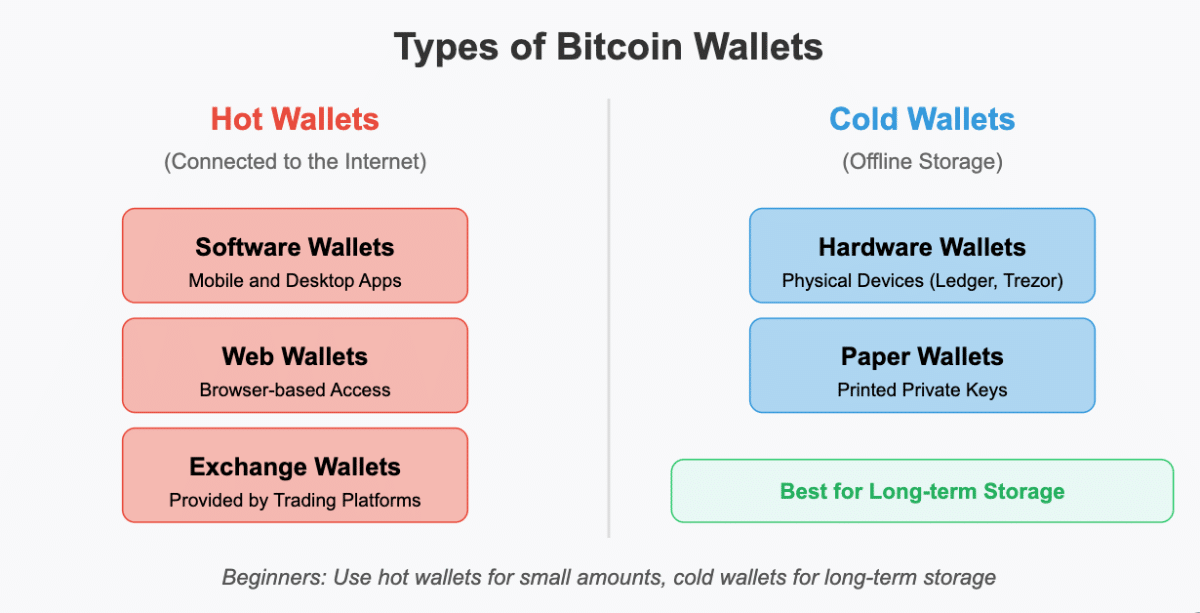
Let’s now have a look at the types of wallets:
Hot Wallets (connected to the internet)
- Software wallets: Applications on your computer or smartphone
- Web wallets: Browser-based wallets accessed through websites
- Exchange wallets: Provided by cryptocurrency exchanges
Cold Wallets (offline storage)
- Hardware wallets: Physical devices like Ledger or Trezor
- Paper wallets: Private keys printed on paper (not recommended for beginners)
For beginners, a combination approach works best: use a hot wallet for small amounts you might spend and a cold wallet for long-term storage.
Popular Wallet Options
| Wallet Type | Examples | Best For | Security Level |
| Hardware (Cold) | Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T | Long-term storage | Highest |
| Mobile App (Hot) | Bitcoin Wallet, Trust Wallet | Everyday transactions | Medium |
| Desktop (Hot) | Electrum, Exodus | Regular access with better security than the web | Medium-High |
| Exchange (Hot) | Coinbase, Binance | Active trading | Lowest |
Choosing a Cryptocurrency Exchange
Exchanges are platforms where you can buy, sell, and sometimes store cryptocurrency. Your choice of exchange impacts factors like fees, available payment methods, and security.
When selecting an exchange, security should be your top priority. Look for platforms that maintain insurance policies against theft, store the majority of assets in cold storage, and have established strong security track records without major hacks.
Next, carefully compare the fee structures, as they significantly impact your overall costs. Trading fees typically range from 0.1% to 4% but don’t forget to check deposit and withdrawal fees, which can sometimes exceed trading costs.
User experience matters, too, especially for beginners. If you plan to trade on the go, consider the interface complexity, quality of customer support (including response times), and mobile app functionality. If you might diversify beyond Bitcoin in the future, check the variety of cryptocurrencies available on the platform to avoid needing multiple accounts.
Be aware of geographical restrictions, as not all exchanges operate in every country, and some features may be limited based on your location.
Finally, prioritize exchanges with proper regulatory compliance in your jurisdiction. Regulated exchanges provide additional consumer protections and are more likely to follow standard financial security practices, though they typically require more extensive identity verification.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Exchanges
Let’s compare centralized vs. decentralized exchanges to make things clearer:
| Feature | Centralized Exchanges (CEX) | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) |
| Operation | Run by companies acting as intermediaries | Operate without a central authority using smart contracts |
| Ease of Use | More intuitive interfaces with guided processes | Often more complex with a steeper learning curve |
| Liquidity | Higher trading volumes and better liquidity | Generally lower liquidity with fewer trading pairs |
| Privacy | Require full identity verification (KYC) | Typically offer more privacy with reduced or no KYC |
| Security Model | You trust the exchange to secure your funds | You maintain custody of your funds during trading |
| Support | Customer service teams are available | Limited or community-based support |
| Speed | Faster transaction processing | Can be slower depending on blockchain congestion |
| Examples | Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, Gemini | Bisq, RoboSats, Uniswap (for other cryptocurrencies) |
If you are a beginner, you should start with a reputable centralized exchange due to its ease of use and better support options. As you gain experience and confidence, you might explore decentralized alternatives for their privacy and self-custody benefits.
Understanding Fees and Costs
Always keep in mind that buying BTC is not a straightforward process, and it involves several types of fees that can impact your total cost:
- Trading fees: The exchange’s commission on your purchase (0.1-4%)
- Payment method fees: Credit cards (3-5%), bank transfers (0-1.5%)
- Withdrawal fees: Charges for moving Bitcoin to your personal wallet (varies)
- Network fees: Transaction fees paid to Bitcoin miners (highly variable)
To minimize fees, you can use bank transfers instead of credit cards when possible or make fewer, larger purchases instead of many small ones. Also, consider exchanges with fee discounts for high-volume traders and try to time withdrawals during periods of low network congestion.
Step-by-Step Guide to Buying Bitcoin
First of all, you need to create an account. Start by choosing an exchange, some of the popular ones are the ones we mentioned earlier, like Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Gemini. After choosing an exchange, sign up. Provide your email and create a strong password. Don’t forget to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) using an app like Google Authenticator.
After that, complete the verification process. The Know Your Customer (KYC) process typically requires:
- Government-issued photo ID (passport, driver’s license)
- Proof of address (utility bill, bank statement)
- Social Security number (in the US)
- Sometimes, a selfie or video verification
Verification can take anywhere from minutes to several days, depending on the exchange and verification volume.
Depositing Funds
Once verified, you’ll need to fund your exchange account. Below, you will find a table where we compare payment methods:
| Method | Speed | Fees | Limits | Privacy |
| Bank Transfer (ACH) | 3-5 days | Low (0-1.5%) | Highest | Low |
| Debit Card | Instant | Medium (2-3.5%) | Medium | Low |
| Credit Card | Instant | High (3-5%) | Medium | Low |
| PayPal | Instant | Medium-High (2.5-4%) | Medium | Low |
| Cash (Bitcoin ATM) | Instant | Very High (7-15%) | Low-Medium | Medium-High |
| Wire Transfer | 1-2 days | Fixed fee ($10-35) | Highest | Low |
Always double-check all account numbers and wallet addresses before confirming any transaction. A single incorrect character can send your funds to the wrong destination, and you will not be able to recover them.
It’s wise to start with a small test transaction before transferring large amounts. This lets you confirm that everything works correctly and gives you confidence before committing significant funds.
Also, be aware that many credit card companies treat cryptocurrency purchases as cash advances. This means you’ll likely face higher fees and interest rates that begin accruing immediately, unlike regular purchases that have grace periods.
And never forget that you must not share your banking credentials with anyone claiming to help you make a deposit. Legitimate exchanges and wallet providers will never ask for your banking passwords, PIN codes, or other sensitive information. Anyone requesting such details is likely attempting fraud.
Placing Your First Bitcoin Order
Exchanges offer different order types with varying complexity. The first one is a market order, where you buy immediately at the current market price, or a limit order, when you set a maximum price you’re willing to pay.
For your first purchase, a simple market order is usually best:
- Select Bitcoin (BTC) as the cryptocurrency to purchase
- Choose “Buy” or “Market Buy”
- Enter the amount in your local currency or in Bitcoin
- Review the fees and total cost
- Confirm your purchase
After purchase, your Bitcoin will appear in your exchange wallet. For security, consider transferring larger amounts to your personal wallet.
Can You Buy Bitcoin Anonymously?
While completely anonymous Bitcoin purchases are difficult, several options still exist. Bitcoin ATMs offer some anonymity, with many requiring only phone verification for smaller amounts. Though convenient, with over 30,000 machines worldwide, they charge steep fees of 7-15%.
Peer-to-peer platforms like Peach Bitcoin, Bisq, or RoboSats provide another option by connecting buyers and sellers directly. Some facilitate cash trades in person or bank deposits and use reputation systems to reduce fraud risk, though transactions may include higher premiums and longer completion times.
Some buyers arrange local Bitcoin meetups for in-person cash trades, but this requires extreme caution and ideally using platforms with escrow services. It’s important to remember that more anonymous purchase methods typically involve higher fees, increased complexity, and potentially greater security risks compared to standard exchange purchases.
Storing and Securing Your Bitcoin
Moving your Bitcoin from an exchange to a personal wallet is crucial for security. Major exchanges have been hacked in the past, causing customers to lose funds. If you are interested, you can read about the biggest digital heist here.
The cryptocurrency community has a saying: “Not your keys, not your coins.” When your Bitcoin is on an exchange, the exchange controls the private keys. By moving to a personal wallet, you take control of your own private keys, which means:
- You’re protected if the exchange is hacked or goes bankrupt
- Your account can’t be frozen or restricted
- You don’t need permission to access or send your Bitcoin
- You’re not exposed to exchange downtime or technical issues
Transferring Bitcoin from an exchange to your personal wallet begins with setting up your wallet by following the provider’s instructions.
Next, locate your wallet’s receiving address—a string of letters and numbers like 3J57t1XpEZ73CZmQvfksriyiWrnqLhGTLy. On the exchange, start a withdrawal and carefully enter this wallet address, as mistakes can’t be reversed.
Select your preferred network fee, balancing cost against speed—higher fees typically result in faster confirmations. Confirm and authorize the withdrawal, which may require 2FA for security. After initiating the transfer, you’ll need to wait for confirmation, which generally takes between 10-60 minutes, depending on network congestion and your chosen fee.
Finally, verify that your Bitcoin has arrived by checking your personal wallet balance. For your first transfer, we suggest you send a small test amount before moving larger sums to ensure everything works correctly.
Latest Bitcoin News
Understanding Bitcoin Fees and Transaction Costs
Bitcoin transaction fees are paid to miners who process and secure transactions. These fees vary based on network congestion. In case of low congestion, the cost is as little as $0.50-2 per transaction. In case of high congestion, it can exceed $50 per transaction during peak times.
Remember that several strategies can help minimize fees:
- Use exchanges that cover withdrawal fees
- Time your withdrawals during weekends or off-peak hours
- Consider using the Lightning Network for small transactions (near-instant and minimal fees)
- Use wallet software that allows custom fee settings
- Be patient if not urgent—lower fee transactions take longer but still go through
Best Security Practices
Properly securing your Bitcoin requires multiple layers of protection. Start by using strong, unique passwords for all accounts. Enable 2FA using an authenticator app rather than SMS, which is vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks.
Your recovery phrase (seed phrase) demands additional care: write it down on paper (never store it digitally), and keep copies in multiple secure locations, never share it with anyone. For significant holdings, consider splitting them across different physical locations.
Remember to update your wallet software and device operating systems regularly to protect against security vulnerabilities. For larger amounts, consider using dedicated devices that aren’t used for everyday browsing or email.
Finally, keep an eye out for phishing attempts targeting crypto users—these have become increasingly common, with attackers creating convincing fake websites and sending deceptive emails claiming to be from exchanges or wallet providers.
What to Do If You Lose Access to Your Bitcoin
There are several recovery options; it just depends on what was lost:
Lost Password to Exchange Account
If you’ve forgotten your exchange account password, use the account recovery process, which typically involves clicking on a “Forgot Password” link. You’ll need to provide identity verification documents to prove ownership of the account, often similar to those used during your initial signup.
Most major exchanges have customer support teams who can help guide you through this process, though response times vary considerably between platforms.
Lost Access to Hardware Wallet
When you’ve lost or damaged your hardware wallet but still have your recovery phrase, you can restore access to your Bitcoin by purchasing a new compatible wallet.
Enter your backup recovery phrase during the setup process of the new device, and follow the wallet manufacturer’s specific recovery instructions. This will recreate the same private keys on your new device, giving you full access to your funds.
Lost Recovery Phrase
Unfortunately, if both your wallet device and recovery phrase are lost, your Bitcoin is likely unrecoverable. This permanent loss shows you the critical importance of secure, redundant backups of your recovery phrase.
Unlike traditional financial services, no central authority can reset your access or recover your funds—the security that makes Bitcoin resistant to censorship also means responsibility rests entirely with you.
Exchange Shutdown
If an exchange where you hold Bitcoin shuts down, monitor all official communication channels for information about the liquidation process. Contact the legal representatives handling claims, which might include bankruptcy trustees or administrators appointed by courts.
Be prepared to file detailed documentation proving your ownership of funds on the platform, including account statements, transaction histories, and correspondence with the exchange. This process often takes years to resolve and may result in only partial recovery of funds.
Using and Managing Your Bitcoin
When it comes to Bitcoin management, there are two primary approaches to consider: selling your Bitcoin when you’re ready to cash out or implementing long-term investment strategies. Let’s explore both options.
Selling Your Bitcoin
Selling Bitcoin is the most common approach. First, transfer your Bitcoin to the exchange if you’ve stored it in a personal wallet. Then place a sell order for your desired amount, choosing between a market sell (immediate sale at current price) or limit sell (sale when Bitcoin reaches your specified price). Once the sale is completed, withdraw the funds to your connected bank account, which typically takes 1-3 business days.
Peer-to-peer selling offers another option with potentially better rates and more payment flexibility. List your Bitcoin on P2P platforms and select your preferred payment method, then utilize the platform’s escrow service to secure the transaction. Only release the Bitcoin after confirming you’ve received payment, which protects both parties from fraud.
If you need immediate cash, some Bitcoin ATMs support selling functionality. While these machines charge higher fees (typically 5-10%), they provide the advantage of instant cash access without bank transfers.
Remember that in most countries, selling Bitcoin triggers tax obligations. Your profits are typically subject to capital gains tax, with rates varying based on your holding period and tax bracket.
Maintain records of all purchases and sales, consider using specialized crypto tax software to track complex transaction histories, and consult with a tax professional familiar with regulations in your jurisdiction.
Investing and Holding Strategies
Long-term holding, often called “HODLing,” involves buying Bitcoin and keeping it for years regardless of price fluctuations. This strategy comes from a belief in Bitcoin’s long-term appreciation potential and simplifies your approach with fewer tax events and less active management. Many long-term holders store their Bitcoin in cold wallets and essentially “forget” about it for extended periods.
For those seeking a balanced approach, dollar-cost averaging (DCA) offers a methodical investment strategy. By investing fixed amounts at regular intervals regardless of price, you reduce the impact of volatility and remove emotional decision-making from the equation. For example, investing $100 weekly rather than $400 monthly spreads your entry points across different price levels. Many exchanges now offer automatic recurring purchase features that make this strategy effortless to implement.
Effective risk management is always a priority, regardless of the strategy you choose. Only invest funds you can genuinely afford to lose, and consider limiting Bitcoin to a reasonable percentage of your overall investment portfolio (many financial advisors suggest 1-5% for speculative investments).
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Buying Bitcoin

Let’s start with FOMO buying, which represents one of the most common mistakes. Buying based on fear of missing out during price rallies often leads to buying at market peaks, followed by major losses when corrections occur. Instead, develop a measured investment strategy based on research rather than emotional reactions to market movements.
Neglecting security creates unnecessary risks with your holdings. Keeping large amounts on exchanges exposes you to platform hacks, while using weak passwords makes your accounts vulnerable to attacks. Implement strong security practices, including hardware wallets for significant amounts and unique, complex passwords for all accounts.
Losing recovery phrases can result in permanent Bitcoin loss. Your recovery phrase serves as the master key to your wallet, and without it, there’s no way to regain access if your device fails or gets lost. Store multiple copies in secure, private locations, preferably offline and protected from environmental damage.
Sending to incorrect addresses remains a significant danger since Bitcoin transactions cannot be reversed. Always triple-check recipient addresses before confirming any transaction. Many experienced users copy-paste addresses to avoid typos and send small test amounts before larger transfers.
Overlooking fees can substantially impact your actual returns. Beyond exchange fees, consider withdrawal fees, network transaction fees, and conversion costs between cryptocurrencies and fiat. Calculate the total cost of each transaction to avoid surprises and determine if smaller, more frequent purchases make sense given the fee structures.
Falling for scams happens even to experienced cryptocurrency users. Be extremely skeptical of promises of guaranteed returns, free Bitcoin giveaways, or investment opportunities requiring urgent action. Legitimate investments never guarantee specific returns, and no one needs your private keys to send you cryptocurrency.
Ignoring tax implications creates potential legal problems. In most jurisdictions, Bitcoin transactions are taxable events that must be reported. Keep detailed records of all purchases, sales, and trades, as tax authorities increasingly focus on cryptocurrency compliance.
Overinvesting occurs when enthusiasm overcomes prudent financial planning. Never invest more in Bitcoin than you can afford to lose, as cryptocurrency remains a highly volatile asset class. Determine a reasonable allocation based on your overall financial situation and risk tolerance.
Sharing private keys or recovery phrases with others guarantees eventual theft. No legitimate service ever needs this information—anyone requesting it is attempting to steal your funds. Treat your private keys with the same security you would use for banking passwords or home safe combinations.
Conclusion
Buying Bitcoin has evolved from a complex technical process to an accessible investment option for everyone. This guide has walked you through every step, from understanding Bitcoin’s value proposition and setting up secure wallets to choosing the right exchange, completing purchases, and implementing proper security measures. We’ve covered various buying methods, storage options, investment strategies, and common pitfalls to avoid.
Whether you’re interested in Bitcoin as a long-term investment, a hedge against inflation, or simply want to understand this technology, the entry barriers have never been lower. The key is to start small, prioritize security, and continue learning as you gain experience.
If you are ready to begin, start by setting up a wallet, selecting a reputable exchange, and making a small initial purchase to familiarize yourself with the process. Remember that proper research and security practices are your best allies during this process.

