Many traders prefer Bitcoin futures, a type of financial derivative, because they offer exposure to its price movements without having to hold it directly. With futures, investors don’t have to worry as much about custody issues, exchange hacks, or losing access to their crypto wallets. In light of recent collapses of cryptocurrency exchanges and regular major hacks, some investors argue that it’s simply too risky to use these kinds of platforms.
Let’s look at Bitcoin futures and see how they can offer investors an alternate path to investments in cryptocurrency.
Understanding Bitcoin Futures
To understand Bitcoin futures, we need to detail exactly what a futures contract is. Futures fall under a category of investments called derivatives. A derivative is a financial instrument that has its value derived (hence the name) from an underlying asset, in this case, cryptocurrency. A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to exchange the equivalent value of an asset in fiat currency on a future date. Futures trading is common across many different asset classes such as stocks, oil, gold, and other commodities.
In simple terms, a futures contract is a bet on the price of an asset going up or down by a future date. Your resulting profits or losses are based on whether your bet was right or wrong.
How Bitcoin Futures Work
Let’s use the price of Bitcoin as an example of a futures contract investment. If an investor bets on the price of one Bitcoin increasing by a specified future date, this is known as “going long.” Conversely, if they think it will drop by the agreed date, it’s called “going short.”
When an investor goes long on a futures contract and the price rises as predicted, they can simply sell the contract later at a higher price. Shorting a futures contract involves selling a contract with the hope of buying it back later at a lower price to lock in a profit.
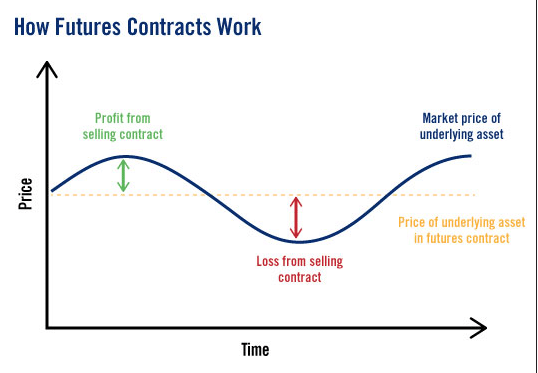
Futures contracts can be perpetual or have a fixed expiration date. In a traditional expiration-date-based contract, parties to the contract settle based on the price of the asset on the expiration date. Perpetual futures contracts have no expiration or settlement date, so they are designed to be continuous in nature. As a result, a person can hold onto the contract indefinitely.
Perpetual contracts use a fee paid by one side of the contract to the other side to maintain a price balance between the futures contract and the underlying spot market. This involves regular payments between long and short positions to make sure that the price of the contract stays aligned with the spot price (the price of an asset at a specific point in time).
The History of Bitcoin Futures
The very first Bitcoin futures were sold on the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in December 2017. They were discontinued in 2019 due to low trading volume and a decline in interest in the product but were restarted again in 2024.
Crypto futures for both Bitcoin and Ethereum were announced in October, 2017 by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Investors were able to buy futures contracts starting in December of the same year. While the CME Group offers reference rates for several other cryptocurrencies, it currently offers futures contracts only for Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Pros and Cons of Trading Bitcoin Futures
Getting involved with Bitcoin futures can be a great alternative to owning cryptocurrency outright. However, it’s important to balance the excitement of a new opportunity with a thorough understanding of the risks involved.
Pros
Profit in both bull and bear markets: Futures contracts allow traders to profit whether prices rise or fall. It all depends on accurately predicting market movements. Unlike traditional buy-and-hold investing, money can be made in both up and down markets.
Hedging: Futures contracts can act as a type of insurance policy (or hedge) against price movements that would otherwise be a liability. For example, if you hold an amount of Bitcoin as an asset and anticipate a short-term price drop, you could go short with a futures contract to try to offset losses.
Leverage: Futures trading allows for leverage, meaning that traders can control a large contract value with a comparatively small upfront deposit (called margin). So if the contract value is $100,000 and the margin requirement is $10,000, then the leverage is 10:1. As a result, if you predict the price of Bitcoin in a futures contract will rise, and you’re correct, your profit is amplified by a factor of 10.
Cons
Leverage: Leverage can certainly amplify profits dramatically, but it can also amplify losses just as easily. If your prediction about a price movement is wrong, your losses will be amplified by the same factor, making high-leverage trading extraordinarily risky.
Liquidation: If your loss passes a threshold set by the contract, your position can be closed (or liquidated), your margin will likely be wiped out, and, depending on the contract’s terms, you could also face additional fees.
Tax implications: Crypto futures profits are treated as Section 1256 contracts by the IRS, meaning that they are subject to the 60/40 rule. This rule states that 60 percent of your profits are taxed as long-term capital gains, and the remaining 40 percent are taxed as short-term gains. State rules vary by jurisdiction.
Regulatory considerations: On the regulatory side, federal agencies regulate crypto futures similar to regulating other commodities. The primary agency involved in crypto futures regulation is the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). It’s important to consult with tax and legal professionals to ensure compliance with applicable laws.
Popular Bitcoin Future Exchanges
Several crypto exchanges offer Bitcoin futures trading. When choosing a crypto futures exchange, you should look for an exchange that has good security, a well-designed user interface, high liquidity, reasonable fees, and leverage levels appropriate to your risk tolerance. We have previously explored a wider range of the best crypto futures trading platforms.
Below are 4 of the most popular Bitcoin futures exchanges.
1. Binance
Trading volume: $43,000,000,000+
Fees: Maker – .02%, Taker – .04%
Binance is the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange. Binance Futures, the derivatives arm of Binance, dominates the futures trading market with a daily trading volume more than double that of its closest rival. This is largely because of its strong reputation and massive selection of more than 340 derivative trading pairs (pairs of assets that can be exchanged for each other) with a wide range of cryptocurrencies. Binance offers high-leverage options for traders comfortable with higher-risk trading, multiple order and contract types, and a competitive fee structure.
2. Bybit
Trading volume: $16,000,000,000+
Fees: Maker – .02%, Take – .055%
Bybit is comparable to Binance in terms of currencies listed and trading products, but where Bybit differs is that futures trading is the central feature of the platform. While it has since launched spot trading, it has focused on futures from the very beginning. Bybit offers futures trading for both Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as numerous altcoins. For the high-risk trader, Bybit offers up to 100x leverage on select futures contracts.
3. OKX
Trading volume: $19,000,000,000+
Fees: Maker – .14%, Taker – .23%
OKX is another popular crypto exchange offering similar features to its competitors such as trading in major cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum as well as altcoins, futures contracts, and high leverage limits. Where OKX differentiates itself is in its fee structure. Traders can purchase OKB, OKX’s proprietary token, to trade with significantly reduced fees. Fee reductions can also be obtained through high trading volume.
4. MEXC
Trading volume: $15,000,000,000+
Fees: Maker – 0%, Taker – .02%
MEXC is a trading platform that offers traders both perpetual and traditional futures contracts. This exchange differentiates itself from its competitors in several unique ways. The first is its advanced trading engine that can handle high trading volumes with minimal latency. Another thing that sets MEXC apart is its security measures. It has a very rigorous KYC (Know Your Customer) process that ensures excellent compliance and security for its customers. Finally, it offers some of the lowest fees on the market, so it’s a strong choice for especially cost-conscious traders.
What Are Bitcoin Futures Options?
Another way to trade Bitcoin futures is through options. An option gives the holder the right to buy or sell a Bitcoin futures contract at a specified price by a certain date. Where an option differs from a futures contract is that the holder has the right, but not the obligation, to exercise the contract. When the expiration date is reached, they have the option (hence the name) to buy or sell the contract, but they are not required to. Options are essentially derivatives of derivatives.
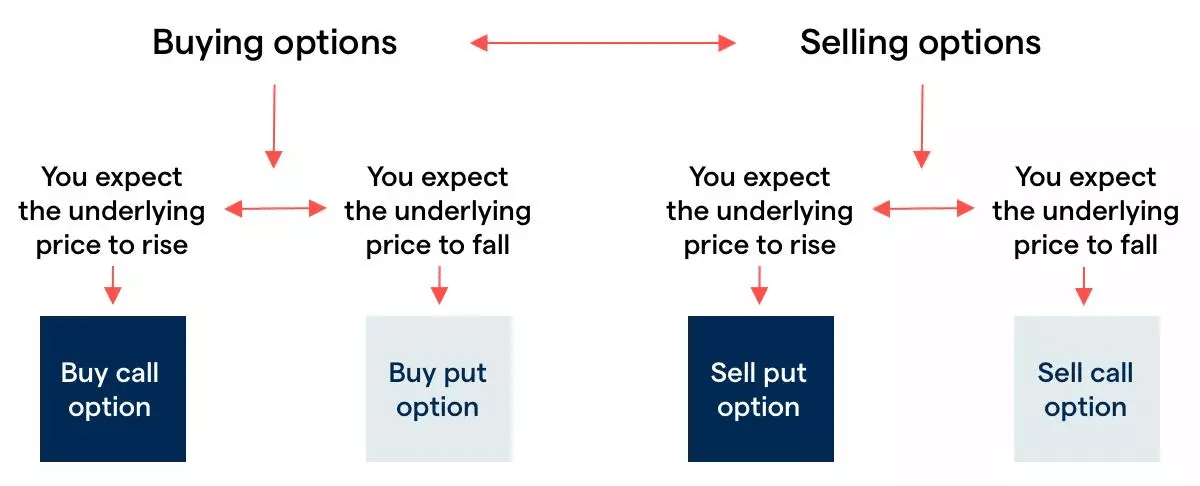
There are two types of options: puts and calls. A call option gives the buyer the right to buy the futures contract at a specified strike price. If the price of the underlying futures contract is higher than the strike price at the expiration date, the buyer can exercise the option to purchase the futures contract at the strike price. Note that while stock options typically cover 100 shares per contract, each futures option generally only corresponds to one contract.
A put option gives the option buyer the right to sell the underlying contract at the strike price. If the price of the futures contract is below the strike price at expiration, then the buyer can exercise the option to sell the contract at the strike price.
By paying a premium for the option, the buyer gains protection from price fluctuations against unfavorable price movements. If the option is not exercised by expiration, the seller keeps the premium.
Are Bitcoin Futures Right for You?
Cryptocurrencies are reaching mainstream acceptance as traditional investment vehicles like futures and options become available to them. These derivatives allow investors the opportunity to invest in cryptocurrencies without actually having to own the asset itself. While offering additional opportunities, it also presents additional risks, making thorough research and due diligence essential before diving in.
FAQs
What is a Bitcoin futures contract?
A Bitcoin futures contract is an agreement between two parties to speculate on the price of Bitcoin by agreeing to buy or sell it at a specific price on a future date, settled in fiat currency like USD.
What is a Bitcoin futures option?
A Bitcoin futures option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a Bitcoin futures contract at a specified price (the strike price) by a certain date (the expiration date).
What crypto futures exchange has the highest trading volume?
Binance has the largest trading volume of any crypto futures exchange.
Who regulates crypto futures?
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) regulates crypto futures in the U.S.
Do I have to pay taxes on Bitcoin futures profits?
Yes. They are taxed by the federal government as capital gains under Section 1256, with 60% taxed as long-term gains and 40% taxed as short-term gains.
References
- Cryptocurrency Futures: Definition and How They Work on Exchanges – Investopedia
- What Are Perpetual Futures and How Do They Work? – Highstrike
- Cboe Bitcoin Futures Open For Trading – PR Newswire
- Self-Regulatory Organizations; NYSE Arca, Inc.; Notice of Filing of Amendment No. 2 to a Proposed Rule Change To List and Trade Shares of the Bitwise Bitcoin ETF Under NYSE Arca Rule 8.201-E (Commodity-Based Trust Shares) – Federal Register
- CME Group Announces Launch of Bitcoin Futures – CME Group
- Crypto Derivatives – Options, Futures & Understanding Taxation – ClearTax
- What is a Bitcoin Futures ETF? – CFTC.gov
- Top Cryptocurrency Spot Exchanges – CoinMarketCap
- OKX Futures Statistics – CoinGecko
- Trading Fees – OKX.com
- What Are Crypto Derivatives? Type, Pros, and Cons – Forbes
- Bitcoin spot vs. derivatives trading: What’s the difference?

