Ethereum futures are financial contracts that let you buy or sell ETH at a set price on a future date, without actually owning any cryptocurrency. They’re essentially a bet on where Ethereum’s price is headed, and they’ve exploded in popularity for good reason.
If you already hold ETH, futures can act as an insurance policy against market crashes. And if you’re looking to diversify beyond Bitcoin, futures let you dip your toes into Ethereum without diving all the way in.
Whether you want to speculate, hedge, or simply understand this powerful financial tool, we’ll explain exactly how Ethereum futures work, compare the different types available in 2025, and show you step-by-step how to start trading them.
Key Takeaways
What Are Futures Contracts?

Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a specific price on a predetermined future date. Unlike forward contracts, which are customized and traded over-the-counter (OTC), futures contracts have standardized terms and trade on regulated exchanges, making them more accessible and liquid.
Futures contracts were originally developed for agricultural commodities but have expanded to include financial instruments, currencies, and now cryptocurrencies like Ethereum.
When trading Ethereum futures, you’re not buying or selling the actual cryptocurrency. Instead, you’re speculating on Ether’s price movements without needing to own the underlying asset. This key distinction has several advantages:
- You can profit from both rising and falling markets.
- You can leverage your positions to control more Ethereum with less capital.
- You can trade on regulated exchanges with robust security measures.
- You can avoid the complexities of cryptocurrency custody and wallets.
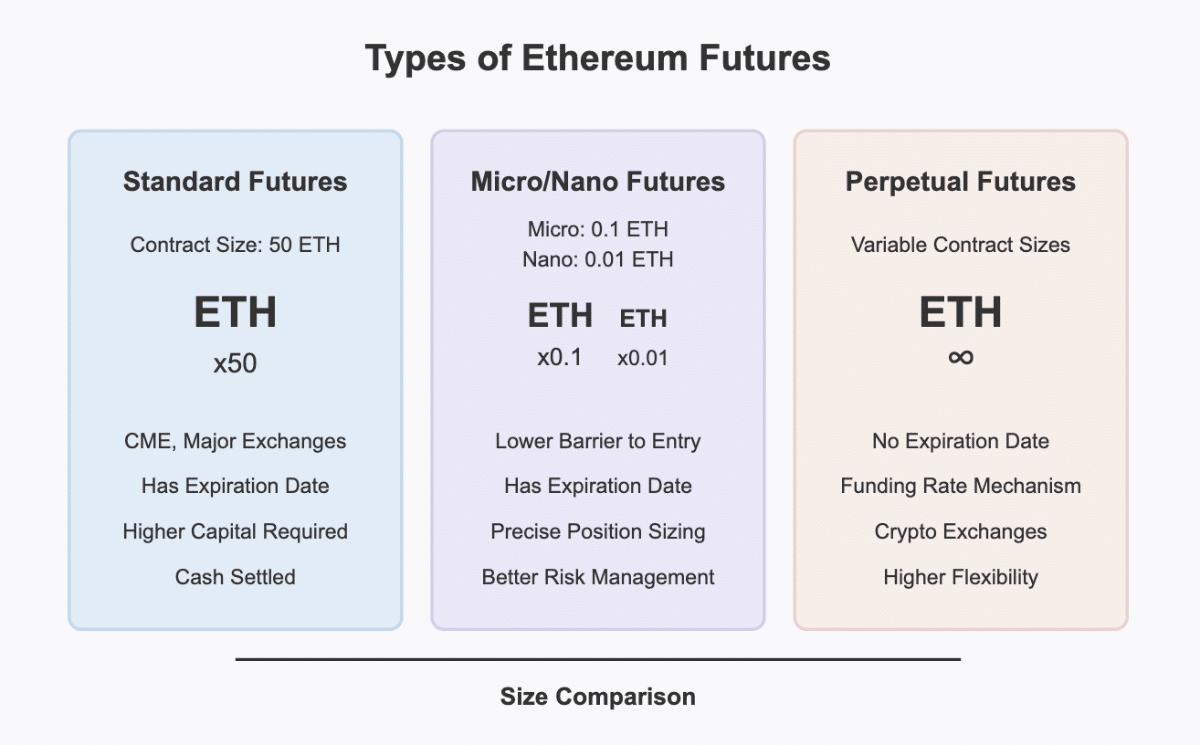
Types of Ethereum Futures
There are several types of ETH futures, and we discuss them in this section:
Standard Ethereum Futures
Regulated exchanges like CME Group offer standard Ethereum futures contracts. These contracts have specific specifications:
- Contract Size: Each contract represents 50 Ether
- Price Quotation: US dollars per Ether
- Minimum Price Fluctuation: $0.25 per Ether ($12.50 per contract)
- Trading Hours: Nearly 24/7 trading on CME Globex from Sunday through Friday, 5 PM to 4 PM Central Time
- Settlement: Cash-settled based on the CME CF Ether-Dollar Reference Rate
For example, if Ethereum is trading at $2,000, a single futures contract would have a notional value of $100,000 (50 ETH × $2,000). However, you don’t need $100,000 to trade this contract – you only need to post the required margin, typically a fraction of the contract value.
Micro and Nano Ethereum Futures
To make Ethereum futures more accessible to retail traders, exchanges have introduced smaller contract sizes:
- Micro Ethereum Futures: Represent 1/10th of an Ether (0.1 ETH)
- Nano Ethereum Futures: Represent 1/100th of an Ether (0.01 ETH)
These smaller contracts lower the barrier to entry, allowing traders with smaller accounts to participate in the Ethereum futures market with more precise position sizing and risk management.
Perpetual Futures Contracts
Perpetual futures are a popular innovation in crypto markets that don’t have an expiration date and can be held indefinitely. To keep the contract price aligned with the spot price, these contracts use a funding mechanism.
- When the perpetual price is higher than the spot price, long positions pay short positions
- When the perpetual price is lower than the spot price, short positions pay long positions
This funding rate creates an incentive for traders to push the price toward the spot price. Exchanges like Bitget and Kraken offer perpetual Ethereum futures that have become increasingly popular due to their flexibility.
Ethereum Futures vs. Spot Trading
Understanding the differences between futures and spot trading is crucial for developing an effective trading strategy.
| Feature | Ethereum Futures | Ethereum Spot Trading |
| Ownership | No direct ownership of ETH | Actual ETH ownership |
| Leverage | Typically 10x-100x available | Limited or no leverage |
| Direction | Can profit from price increases and decreases | Primarily profits from price increases |
| Settlement | Cash settlement or physical delivery | Immediate ownership transfer |
| Costs | Trading fees, funding rates (for perpetuals) | Trading fees, gas fees, custody costs |
| Security | Exchange security | Wallet security |
| Regulation | More regulated | Less regulated |
The key advantage of futures trading is leverage. For example, with 10x leverage, a 5% move in Ethereum’s price would result in a 50% profit (or loss) on your invested capital. This amplification works both ways, significantly increasing both potential gains and potential losses.
How Do Ethereum Futures Work?
Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. Most cryptocurrency exchanges offer leverage ranging from 2x to 100x for Ethereum futures.
For example, with 20x leverage, you could control $20,000 worth of Ethereum with just $1,000 of capital. While this amplifies potential profits, it equally magnifies potential losses. A 5% move against your position would result in a loss of 100% of your invested capital with 20x leverage.
Margin Requirements
To trade Ethereum futures, you must maintain sufficient margin in your account. There are two types of margin requirements:
- Initial Margin: The minimum amount required to open a position
- Maintenance Margin: The minimum amount required to keep the position open
If your account equity falls below the maintenance margin due to adverse price movements, you’ll receive a margin call. To avoid liquidation, you’ll need to either deposit additional funds or reduce your position size.
Settlement
Ethereum futures can be settled in two ways:
- Cash Settlement: No physical delivery of Ethereum occurs; instead, profits or losses are settled in cash based on the difference between the contract price and the settlement price.
- Physical Settlement: The underlying Ethereum is delivered to the contract holder at expiration (less common in cryptocurrency futures).
Most Ethereum futures are cash-settled based on a reference rate derived from multiple spot exchanges.
Trading Strategies With Ethereum Futures
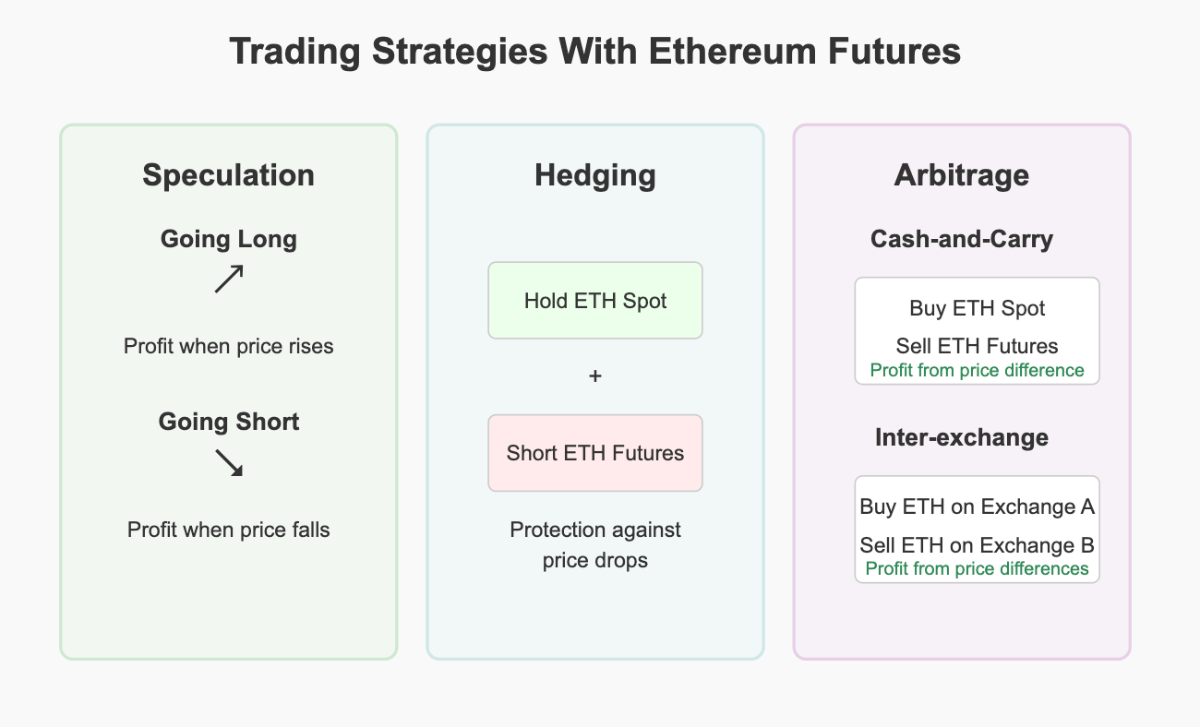
Speculation
The most straightforward strategy is speculation—betting on the future price direction of Ethereum:
- Going Long: If you believe Ethereum’s price will rise, you can buy (go long) futures contracts.
- Going Short: If you expect Ethereum’s price to fall, you can sell (go short) futures contracts.
For example, if you go long one standard Ethereum futures contract at $2,000 and the price rises to $2,200, you’d make a profit of $10,000 (50 ETH × $200).
Hedging
Futures contracts can be used to hedge existing Ethereum holdings against price volatility:
- Protecting Long Positions: If you hold Ethereum and want to protect against a potential price drop, you could short an equivalent amount of futures contracts.
- Locking in Prices: Producers or users of Ethereum-based services can use futures to lock prices for future transactions.
For instance, if you hold 50 ETH worth $100,000 and fear a market downturn, you could short one standard Ethereum futures contract. If Ethereum’s price falls 20%, your spot holdings would lose $20,000 in value, but your futures position would gain approximately $20,000, neutralizing the loss.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences between related markets:
- Cash-and-Carry Arbitrage: Buying spot Ethereum and simultaneously selling futures when the futures price is significantly higher than the spot price plus carrying costs.
- Inter-exchange Arbitrage: Taking advantage of price discrepancies between different exchanges.
These strategies typically require significant capital and strong execution capabilities but can provide relatively low-risk returns.
What are Ethereum Futures ETFs?
Ethereum futures ETFs are investment vehicles that hold Ethereum futures contracts rather than the cryptocurrency itself. These ETFs allow investors to gain exposure to Ethereum’s price movements through traditional brokerage accounts without directly dealing with exchanges or wallets.
In 2024, the approval of Ethereum futures ETFs by regulatory bodies like the SEC marked a milestone for cryptocurrency adoption. Major players like ProShares, VanEck, and Fidelity launched Ethereum futures ETFs, expanding access to a broader range of investors.
Benefits of Ethereum Futures ETFs
Ethereum futures ETFs open the crypto market to a much wider audience through their accessibility. You can simply buy ETF shares through your existing brokerage account, even retirement accounts like IRAs, without creating crypto exchange accounts. This regulatory compliance provides real protection for your investments under established securities laws.
From a practical standpoint, ETF taxation follows familiar securities rules, potentially saving you considerable headaches compared to the complex reporting requirements of direct crypto ownership. Perhaps most importantly for crypto newcomers, ETFs eliminate the intimidating technical hurdles of wallet setup and private key management that trip up many would-be Ethereum investors.
Risks of Ethereum Futures ETFs
While ETFs solve many problems, they introduce some unique challenges worth considering. The contango effect can silently erode your returns when futures prices exceed spot prices, forcing ETFs to roll contracts forward at a loss. This phenomenon is known as “contango bleed” and can affect your investment even when Ethereum’s price remains stable.
Don’t overlook management fees either; while seemingly small (often 0.8-1.5% annually), they compound over time and can significantly impact long-term performance.
Tracking error presents another concern, as the ETF’s price movements may not perfectly mirror Ethereum’s actual performance due to the futures mechanism. ETFs only trade during standard market hours (typically 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM Eastern), potentially leaving you unable to react to major crypto movements that often occur overnight or on weekends.
Getting Started with Ethereum Futures Trading
Selecting the right platform can make or break your Ethereum futures trading experience. Let’s start with CME Group, which stands out for traders seeking regulatory certainty, offering standard-sized contracts (50 ETH) in a fully regulated environment with institutional-grade security.
Kraken can be an appealing choice to traders wanting flexibility, with both traditional and perpetual futures options, plus a user-friendly interface that makes navigating the futures market more approachable.
Bitget is an option for traders seeking variety, featuring USDT-M and USDC-M contracts that allow you to collateralize positions with stablecoins rather than conventional currency.
Beyond the platform itself, you’ll want to carefully evaluate each exchange’s regulatory status (particularly important if you’re in the US), leverage options (ranging from 2x to 100x depending on the platform), fee structure (including both trading and settlement fees), available liquidity (affecting how easily you can enter and exit positions), and security measures (such as cold storage practices and insurance policies).
Account Setup and Funding
Once you’ve chosen your platform, getting started is surprisingly straightforward.
Step 1: Create and verify your exchange account
First, create your exchange account, which typically takes just 5-10 minutes. You’ll then need to verify your identity through the KYC process. Have your government ID ready, and expect this step to take anywhere from a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the exchange’s verification queue.
Step 2: Fund your account
Once verified, fund your account with the required collateral. Most platforms accept USD bank transfers, but you can often fund with USDT, USDC, or even other cryptocurrencies for faster access. Some exchanges separate your main and futures accounts, so you’ll need to transfer funds to your futures wallet within the platform explicitly.
Step 3: Understand the platform’s margin system
Finally, take time to understand your chosen platform’s margin system. Initial margin requirements (how much you need to open a position) typically range from 5-15% of the contract value, while maintenance margin (the minimum to keep positions open) is usually 3-7%, with liquidation occurring if your account falls below these thresholds.
Latest Trading News
Developing a Trading Strategy
A solid strategy separates successful futures traders from the 80% who lose money. Start with technical analysis by mastering 3-5 key indicators rather than overwhelming yourself with dozens. Many profitable traders rely heavily on support/resistance levels, moving averages, and the RSI indicator to identify optimal entry and exit points.
Don’t ignore fundamental analysis, which becomes increasingly important for longer-term positions; stay informed about Ethereum upgrade timelines, developer activity metrics, and institutional adoption rates that can dramatically affect price. Implement strict stop-loss orders at 5-10% below entry for leveraged positions, never risk more than 1-5% of your account on a single trade, and consider scaling down leverage from the maximum offered to preserve capital during volatility.
Before risking real money, backtest your strategy against at least six months of historical data to gauge its effectiveness across different market conditions. Remember that futures trading amplifies both gains and losses. Start with smaller position sizes (perhaps 25% of what you ultimately intend to trade) until you’ve proven your strategy works in real market conditions.
How Have Ethereum Upgrades Impacted ETH Futures?
Ethereum’s transition to proof-of-stake through “The Merge” in 2022 sent ripples through the futures market that continue today. The shift slashed energy consumption by 99.95%, dramatically improving Ethereum’s environmental credentials and attracting institutional investors who’d previously avoided crypto due to ESG concerns. You’ll notice this institutional interest reflected in futures trading volumes, which jumped 47% in the six months following The Merge.
Beyond environmental impacts, staking yields now play a crucial role in futures pricing. When spot ETH holders can earn 4-5% annually through staking, futures contracts frequently trade at a premium that factors in these opportunity costs. This creates a fascinating dynamic where futures prices reflect expected price movements and incorporate the foregone staking rewards.
The reduced issuance rate post-Merge, dropping from about 4.5% annually to less than 0.5%, has altered supply-demand dynamics. With fewer new ETH entering circulation, upward price pressure has translated into futures contracts trading at higher premiums than historical averages.
Looking ahead, upgrades like sharding (which will increase transaction throughput) and EIP-4844 (which will reduce L2 transaction costs) will likely trigger similar adjustments in futures markets as traders position themselves ahead of these technical milestones. Smart traders are already factoring these roadmap developments into their futures strategies, creating opportunities for those who closely follow Ethereum’s technical evolution.
Outlook for ETH Futures
The Ethereum futures are transforming at high speed. Wall Street giants like BlackRock, JPMorgan, and Goldman Sachs have increased their Ethereum futures trading desks, injecting billions in institutional capital that has doubled market liquidity since 2023. This institutional influx is adding stability and also reshaping market dynamics by reducing volatility and creating deeper orderbooks that benefit all participants.
Regulatory clarity continues to emerge across major markets, with the CFTC and SEC establishing clearer frameworks for cryptocurrency derivatives. While some jurisdictions have embraced these financial innovations, others maintain restrictive approaches. These regulatory developments will determine which exchanges thrive and which struggle to maintain compliance.
Innovation accelerates across the ecosystem as exchanges compete for market share. We’re seeing the emergence of specialized products beyond standard futures: from micro contracts for retail traders to sophisticated options on futures that allow for more nuanced trading strategies. The most notable recent innovations include:
- Weather-based futures that correlate with Ethereum’s energy consumption patterns
- Transaction-fee futures that allow dApp developers to hedge against gas price volatility
- Cross-chain derivatives that enable exposure to Ethereum alongside other L1 blockchains
Perhaps most significantly, the lines between traditional and crypto finance continue to blur. Integrating Ethereum futures into mainstream trading platforms has expanded use cases well beyond speculation. Businesses now use these instruments for treasury management, while DeFi protocols increasingly incorporate futures contracts into their liquidity strategies.
As Ethereum evolves toward greater scalability through sharding and L2 solutions, the futures market will likely undergo parallel transformation, reflecting both new opportunities and unforeseen risks.
Conclusion
Ethereum futures offer traders and investors a powerful tool for gaining exposure to Ethereum price movements without directly holding the cryptocurrency. Whether you’re looking to speculate on price direction, hedge existing positions, or diversify your investment portfolio, futures contracts provide flexibility and leverage unavailable in spot markets.
However, leverage and cash settlement advantages come with increased risk, particularly for inexperienced traders. Before entering the Ethereum futures market, take time to thoroughly understand contract specifications, margin requirements, and the mechanics of futures trading. Start with smaller positions, implement strict risk management rules, and continuously educate yourself about both technical trading strategies and Ethereum’s fundamental developments.
With proper research and risk management, Ethereum futures can be a valuable addition to your cryptocurrency trading arsenal, enabling sophisticated strategies regardless of market direction.