Slippage is one of the most important concepts that crypto traders absolutely need to understand. Because the crypto market is so diverse and volatile, prices often fluctuate dramatically second by second. If you don’t set your settings correctly, you can place an order at one price, only to have it filled at an entirely different one just seconds later. The difference between the two prices is called slippage.
If you aren’t careful, slippage can dramatically impact your bottom line. It doesn’t matter if you are a casual trader or a DeFi aficianado. Sometimes, you will pay more than the expected price, leading to unnecessary losses. Other times, you will get lucky and pay less.
Either way, slippage is something every crypto trader should be aware of. That being said, this article will tell you all about slippage and how you can minimize it in crypto.
Understanding Slippage in Crypto
Slippage occurs when a trade is executed at a price different from the one you intended. This is very common in financial markets, but it is especially noticeable in the crypto market due to the market volatility and relatively low liquidity.
For instance, if you are trying to buy Ethereum during a sudden price surge, you might see your order fill at a higher price than you originally intended. This is what we call negative slippage. On the other hand, if the price drops just before your order goes through, you will automatically pay less. This is positive slippage.
So, why is slippage important in trading?
Slippage affects how much you are really paying. A small amount of slippage can be harmless. However, over time, especially if you do large or frequent trades, slippage can eat into your profits or increase your costs. If you aren’t careful and like to trade coins on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) with low liquidity, you could lose a large portion of your investment in just one transaction due to front-running or just high volatility.
If you know how slippage works and how you can minimize it, you can significantly reduce the risks of trading coins with low liquidity. You can use the information to choose smarter trading strategies, avoid bad timing, and set proper limits to your trades.
In short, understanding how slippage works will help you protect your money.
Why Does Slippage Happen?
Slippage occurs because of two main factors:
- Market volatility: Cryptocurrency prices can change rather rapidly. If the market moves between the moment that you place your order and the moment when it’s executed, slippage can occur.
- Low liquidity: In markets with fewer buy and sell orders, the larger trades can significantly impact the price, which also leads to slippage.
Positive slippage is more likely in volatile markets or when there is an increase in liquidity, which leads to favorable price movements between order placement and execution.
Negative slippage, on the other hand, is more common during periods of high volatility, low liquidity, or when executing large market orders that can impact the asset’s price.
To quantify slippage, you can use the following formulas.
For Buy Orders (when the price goes up):
Slippage (%) = ((Executed Price – Expected Price) / Expected Price) × 100
For Sell Orders (when the price goes down):
Slippage (%) = ((Expected Price – Executed Price) / Expected Price) × 100
Example: If you expected to buy Bitcoin at $30,000, but the order executed at $30,300, here is how the slippage would be calculated:
Slippage = ((30,300 – 30,000) / 30,000) × 100
Slippage = (300 / 30,000) × 100
Slippage = 1%
This means that you experienced 1% negative slippage.
Slippage Examples
Slippage can play out differently depending on where and how you trade. Let’s consider some examples to show how this works.
Example 1: Low Slippage in a Highly Liquid Pool
You want to swap $5,000 USDC for ETH on Uniswap. The trading pair is USDC/ETH, which is one of the most active and liquid pools on the platform.
- Expected price: $2,500 per ETH
- Trade size: $5,000
- Slippage: 0.1%
- Execution price: $2,502.50 per ETH
Since there is a lot of liquidity and the trade isn’t massive relative to the size of the pool, the price movement is minimal. You will end up with nearly what you expected, and the slippage cost is about $5 total. This is considered very low in the crypto world.
Example 2: High Slippage in an Illiquid Pool
You want to trade $5,000 worth of a small altcoin called XYZ on a decentralized exchange. The pair is XYZ/USDT, and the pool only has $30,000 in total liquidity.
- Expected price: $1.00 per XYZ
- Trade size: $5,000
- Slippage: 12%
- Execution price: $1.12 per XYZ
Since the pool is small, your $5,000 order takes a large chunk of the liquidity, which pushes the price up. The actual executed price is $560 over what you expected. You would need the price of XYZ to rise at least 12% just to get back to even. This is negative slippage, and it can be surprisingly harmful to your wallet.
Real-World Examples
Let’s take a look at some real-life losses now.
On Reddit, a trader shared that they attempted to swap $4,800 worth of WETH for Kizuna tokens on Uniswap. Despite saying that he set a slippage tolerance of 0.5%, the transaction resulted in receiving only $3,363.54 worth of Kizuna tokens, so he effectively lost around $1,500 or 30% due to slippage.
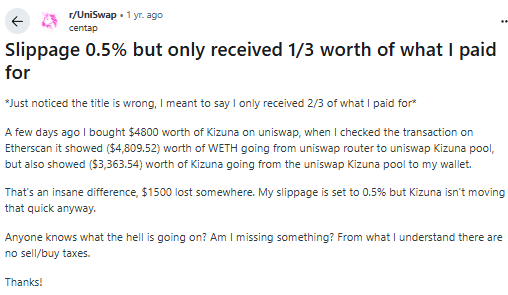
His loss happened because the Kizuna token pool had low liquidity. Large trades in such pools can drastically affect the token price and lead to substantial negative slippage. However, if he in fact did set his slippage tolerance to 0.5%, the transaction should have just failed. He may have mistakenly set his slippage to “Auto,” but it’s also possible that the problem was on Uniswap’s end.
In February 2020, a trader using the Fulcrum platform borrowed 811,000 DAI collaterized with 1,446 ETH, and attempted to swap it for WETH via Kyber. Due to low liquidity and the large trade size, his transaction suffered a massive slippage, so he lost around $250,000.
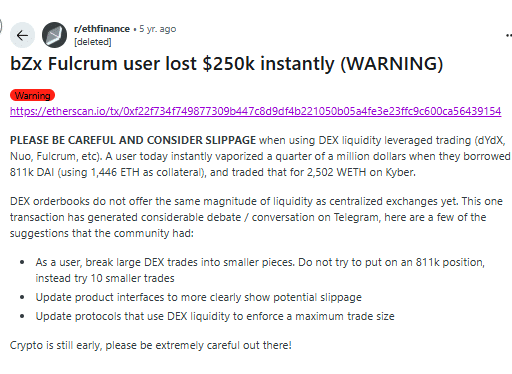
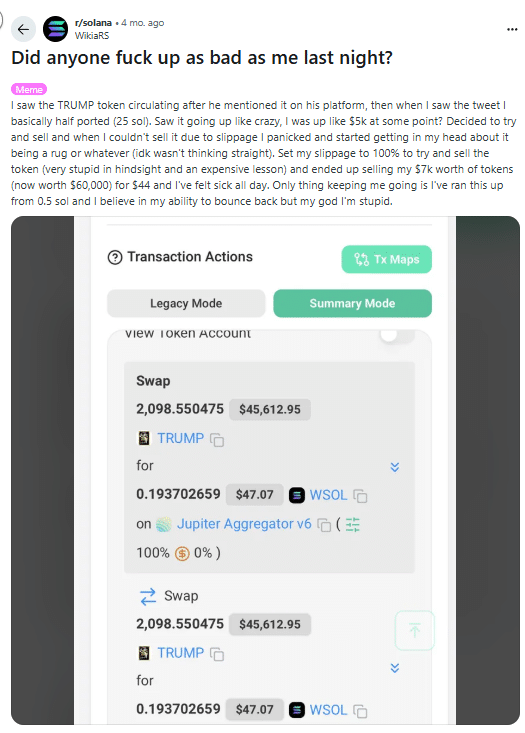
In another case, a trader attempted to sell $7,000 worth of a token with a 100% slippage setting. The transaction was executed at such an unfavorable rate that he received only $44 in return! This may have been caused by a front-running bot taking advantage of the 100% slippage trade.
How to Minimize Slippage in Crypto
The cryptocurrency market is subject to tremendous market fluctuations, which is why it is recommended to minimize slippage when you make trades. Let’s take a look at some tips that will help you avoid excessive slippage.
1. Set Appropriate Slippage Tolerance
On decentralized exchanges like Uniswap, you can define what we call a slippage tolerance. This is the maximum percentage difference you are willing to accept between the expected and actual executed price of a trade. If the price moves beyond your set tolerance, the transaction should fail.
- Default Settings: Uniswap often sets an automatic slippage tolerance between 0.1% and 5%, depending on network conditions and trade size.
- Custom Settings: For more control, you can manually adjust the slippage tolerance.
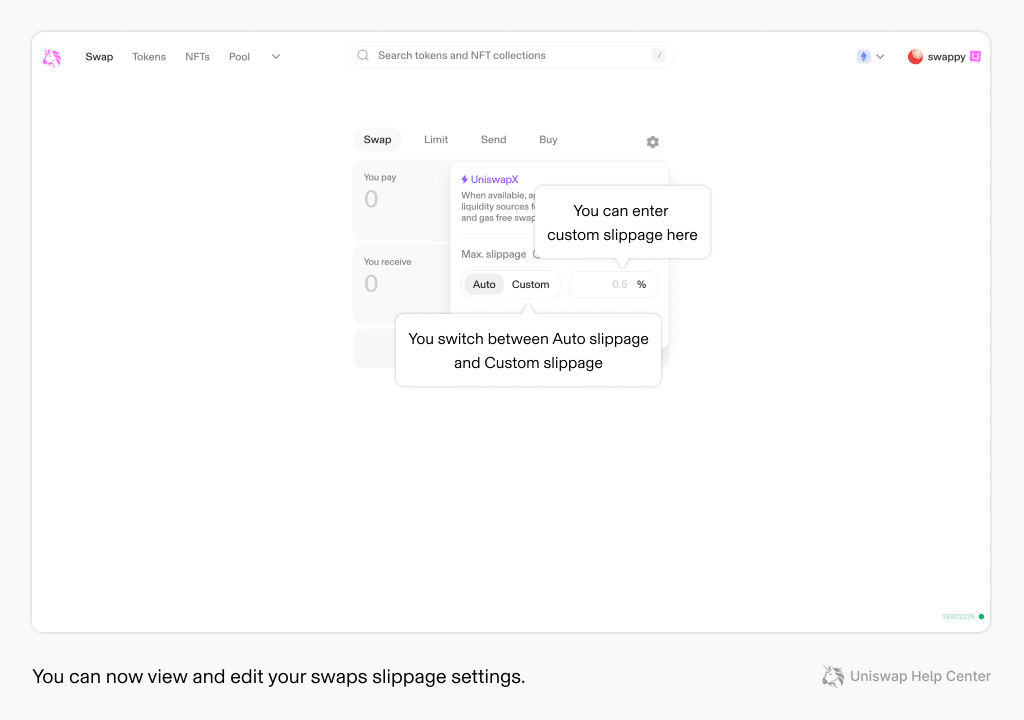
Tips: For low volatility and high liquidity, set a tight tolerance, preferably around 0.1%-0.5%. For high volatility or low liquidity, consider a higher tolerance (e.g., up to 5%), but still be cautious of unfavorable price movements. Trading especially small and illiquid tokens may require even higher slippage tolerance if your transactions fail at or below 5%.
Here is what your slippage will look like in Uniswap:
2. Use Limit Orders
Unlike market orders, limit orders execute only at your specified price or better, therefore eliminating unexpected slippage. This strategy is most effective on centralized exchanges, as well as the few DEXs that support limit orders.
3. Avoid Trading During High Volatility
Price fluctuations are much more pronounced during major news events and market openings. If you want to reduce slippage as much as possible, make sure to trade during calmer periods.
4. Trade in High-Liquidity Pools
Highly-liquid pools can absorb larger trades without significantly impacting the price. Before you trade, check the pool’s liquidity to ensure it can handle your trade size. Many DEXs offer multiple pools for each token, with varying liquidity and trading fees, so make sure you pick the best one for you.
5. Break Down Large Trades Into Smaller Ones
Executing large trades in small increments can minimize market impact and reduce slippage. This approach allows the market to adjust between the trades and gives market participants a chance to get a better price.
6. Gradually Adjust the Slippage Tolerance in Illiquid Pools
When you are dealing with illiquid tokens, it’s often smart to start low. Experienced traders like to begin with a low tolerance of around 0.5%, at least if they aren’t in a major hurry to trade. If the transaction fails, you can slightly increase the tolerance and retry. Continue this process until the transaction succeeds, and make sure you don’t set the tolerance excessively high. It is almost never a good idea to set “Auto” slippage as it could lead to a devastating front-running attack.
Conclusion
Slippage is a natural part of crypto trading, especially when you are using decentralized trading platforms or dealing with highly volatile (or illiquid) tokens. Slippage can sometimes be positive, but it’s much more likely to hurt your wallet.
While you cannot completely eliminate slippage, you can surely reduce its impact. Understanding liquidity, adjusting your slippage settings, and paying close attention to market conditions could save you hundreds or even thousands of dollars over the years.
Just remember: slippage is an inherent risk of trading, but it is one you can manage if you are careful. Keep your trade size reasonable and avoid those volatile moments to stay closer to your maximum price targets. Good luck!
FAQs
What causes slippage in crypto?
Slippage usually happens when there is low liquidity, high volatility, or both. If you have a large trade or the market conditions change fast, you might not get the price you expected.
Is slippage always bad?
Not always. Slippage refers to a change for a better or a worse price. Sometimes, it will work in your favor and get a better price than you requested. This is called positive slippage.
How can I reduce slippage on a DEX like Uniswap?
You can use a lower slippage tolerance, but also trade in high-liquidity pools, and try to avoid peak volatility.
Why does my trade fail due to slippage?
Your trade might fail if the price moves outside your slippage tolerance before confirmation. To fix this, slowly increase your slippage setting or try again when the market is more stable.
Can I completely eliminate slippage?
No. You cannot fully eliminate slippage, especially on DEXs. Still, you can reduce its effect with smart settings and careful timing.