Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are community-driven systems that operate on blockchains without a central governing authority. Instead of a single leader making decisions, rules are enforced by smart contracts that enable collective governance. Interested participants must hold governance tokens, which give them voting rights on proposals and changes to the organization.
| # | Coin | Price | 24h % | Market Cap | Volume | 24h Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
$2,740.68 | -0.17% | $1,163,336,378 | $185,975 |
$2,724.78
―
$2,788.61
|
| 2 |
|
$0.63 | -8.25% | $857,425,009 | $124,087,057 |
$0.63
―
$0.70
|
| 3 |
|
$0.87 | 0.69% | $780,393,137 | $187,297,107 |
$0.85
―
$0.92
|
| 4 |
|
$0.22 | -6.53% | $117,883,615 | $19,488,810 |
$0.22
―
$0.23
|
| 5 |
|
$0.11 | 1.25% | $85,501,267 | $3,737,438 |
$0.11
―
$0.12
|
| 6 |
|
$0.41 | -5.11% | $37,710,872 | $8,261,967 |
$0.41
―
$0.43
|
| 7 |
|
$0.13 | -1.83% | $33,526,740 | $669,931 |
$0.13
―
$0.14
|
| 8 |
|
$18.68 | 0.54% | $32,691,104 | $3,487 |
$17.49
―
$19.10
|
| 9 |
|
$0.0027 | -2.03% | $22,313,873 | $4,033,256 |
$0.0028
―
$0.0029
|
| 10 |
|
$0.29 | -3.02% | $21,538,797 | $4,276,476 |
$0.28
―
$0.30
|
| 11 |
|
$0.03 | -3.25% | $19,822,840 | $4,416 |
$0.03
―
$0.03
|
| 12 |
|
$0.0(5)44 | -1.11% | $18,174,052 | $125,327 |
$0.0(5)44
―
$0.0(5)46
|
| 13 |
|
$0.02 | -2.29% | $17,355,945 | $2,095,784 |
$0.02
―
$0.02
|
| 14 |
|
$0.27 | -5.42% | $16,994,461 | $10,888 |
$0.27
―
$0.29
|
| 15 |
|
$0.06 | 0.53% | $16,443,205 | $331,427 |
$0.05
―
$0.06
|
| 16 |
|
$0.08 | -8.47% | $15,049,500 | $346,016 |
$0.08
―
$0.08
|
| 17 |
|
$0.03 | -0.27% | $11,750,635 | $419,399 |
$0.03
―
$0.03
|
| 18 |
|
$0.0015 | 3.22% | $9,748,153 | $402,712 |
$0.0014
―
$0.0015
|
| 19 |
|
$0.03 | -7.76% | $4,620,034 | $114,319 |
$0.03
―
$0.03
|
| 20 |
|
$0.0(3)35 | -4.95% | $3,191,045 | $301,832 |
$0.0(3)35
―
$0.0(3)37
|
| 21 |
|
$0.04 | -7.06% | $3,064,002 | $1,211,362 |
$0.04
―
$0.04
|
| 22 |
|
$0.0048 | -0.92% | $2,407,217 | $274,103 |
$0.0047
―
$0.0049
|
| 23 |
|
$0.0014 | - | $1,589,695 | - | - |
Kelp DAO Restaked ETH
RSETHCurve DAO
CRVLido DAO
LDOCookie DAO
COOKIEClearpool
CPOOLMy Neighbor Alice
ALICEDAO Maker
DAOT-mac DAO
TMGVictoria VR
VRLumia
LUMIAGold DAO
GOLDAOCult DAO
CULTNumbers Protocol
NUMStake DAO
SDTStar Atlas DAO
POLISBlockasset
BLOCKVAIOT
VAICere Network
CEREAtlas Navi
NAVIIspolink
ISPXCAD Network
XCADOpenOcean
OOESroomAI DAO
SHR0The most famous DAO example was The DAO, a controversial venture capital fund launched in 2016. It raised $150 million from 20,000 investors, but a smart contract vulnerability led to a hack that lost $50 million. Since then, DAOs and their source codes have become much safer, with more transparent rules and active communities that drive innovation, entertainment, and gaming.
Today, DAOs are implemented in many top blockchain networks, enabling everything from social coordination to infrastructure development. In this article, we recommend the best DAO crypto projects to invest in and interrogate the role of DAOs in the future of blockchain technology.
Top DAO Crypto Projects in 2025
Here are our top 5 DAO crypto project picks.
1. Clearpool ($CPOOL)
Clearpool Price Chart
(CPOOL)Clearpool (CPOOL)
Clearpool (CPOOL) is a leading crypto credit marketplace enabling institutional investors to borrow money from decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. According to Bloomberg, Wall Street powerhouse Jane Street uses Clearpool to take on crypto loans sourced from the decentralized ecosystem.
The platform uses a permissionless protocol for firms to raise unsecured liquidity directly sourced from DeFi markets. Meanwhile, it has a separate fully permissioned site called Clearpool Prime that features KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) compliance for wholesale digital asset lending.
CPOOL is Clearpool’s utility and governance token, which allows holders to vote on whitelisting of potential borrowers. This process qualifies participants to earn additional CPOOL tokens through an intelligent contract reward system. Based on the whitepaper, a full system of Clearpool’s DAO is coming soon
Find out more about Clearpool:
2. My Neighbor Alice ($ALICE)
My Neighbor Alice Price Chart
(ALICE)My Neighbor Alice (ALICE)
Another DAO-based crypto project is My Neighbor Alice (ALICE). It’s a metaverse blockchain platform inspired by Animal Crossing and lets token holders vote on game improvements and operational developments.
ALICE, the native token, functions both as a governance token and an in-game currency. Players in the My Neighbor Alice game can earn ALICE tokens by progressing in certain quests, adding a P2E (Play-to-Earn) layer in the gaming experience. Players can then use their tokens to buy special skills and items through the in-game Alice marketplace.
Additionally, My Neighbor Alice incorporates NFTs (non-fungible tokens), allowing users to create avatars and virtual land that are made into unique NFTs. The platform’s source code is open source, enhancing overall transparency regarding the DAO, gaming mechanics, and other programs on the site.
Find out more about My Neighbor Alice:
3. Victoria VR ($VR)
Victoria VR Price Chart
(VR)Victoria VR (VR)
Launched in 2021, Victoria VR (VR) is an Ethereum-based virtual reality platform with an upcoming DAO launch. It’s the first metaverse MMORPG (massive multiplayer online role-playing game) to use the Unreal Engine, a powerful 3D development tool used by leading gaming developers.
According to the project whitepaper, the blockchain game’s development remains centralized to ensure efficiency and stable growth. Once the Victoria VR team decides the platform has established a significant player base and sustainable ecosystem, it will launch the DAO for community-driven upgrades, patches, and feature implementations.
In addition to its governance utility, the VR native token powers the entire Victoria VR ecosystem and can be used to purchase in-game skins, items, and virtual land. Players can also earn VR tokens by completing gaming challenges or staking VR tokens and gaining from the rewards pool.
Find out more about Victoria VR:
4. DAO Maker ($DAO)
DAO Maker Price Chart
(DAO)DAO Maker (DAO)
DAO Maker (DAO) is a decentralized VC platform and crypto launchpad that has raised over $90 million to help develop various DAO-based projects. In fact, Clearpool and Victoria VR had their IDOs (Initial DEX Offerings) on DAO Maker.
The decentralized app features two types of offering systems: Public and Private. Users can participate in token IDOs in the Public Offering System by depositing Tether (USDT) or DAO tokens. DAO token deposits boost the user’s allocation by 500%. In contrast, the Private Offering System provides guaranteed allocations based on a lottery mechanism.
Since its launch, over 1.1 million crypto wallets have connected to the DAO Maker platform, leading to over 300,000 KYC-verified users. Due to its cross-chain compatibility with leading networks like BNB Chain, Solana, and Arbitrum One, the token launchpad remains a popular retail crypto venture investing platform.
Find out more about DAO Maker:
5. Lumia ($LUMIA)
Lumia (LUMIA)
The Lumia DAO requires various roles, each of which is integral to its operations. Liquidity Nodes, for instance, are key players in the system and provide liquidity from various exchanges by locking up their native LUMIA tokens. The whitepaper lists 13 core roles in the LUMIA DAO, from governance stakers to researchers and analysts.
Staying committed to providing the best exchange rates through various platforms, Orion has made its decentralized app available to iOS device users through the App Store. With easy cross-chain swaps and a user-friendly interface, the DAO-driven platform aims to be an innovative force in the Web3 space.
Find out more about Lumia:
Best Wallet - Diversify Your Crypto Portfolio
- Easy to Use, Feature-Driven Crypto Wallet
- Get Early Access to Upcoming Token ICOs
- Multi-Chain, Multi-Wallet, Non-Custodial
- Now On App Store, Google Play
- 250,000+ Monthly Active Users
What Is a DAO?
A DAO is a blockchain-based organization that allows people to manage shared goals without a traditional hierarchical structure. Unlike traditional establishments with human management, DAOs are governed by smart contracts that handle everything from how stakeholders submit proposals to how votes are counted.

Individuals can participate in DAO crypto projects by owning their governance tokens. For example, the Shiba Inu (SHIB) ecosystem features a DAO called Doggy DAO. It uses a governance token called BONE, which allows holders to submit and vote on proposals within the meme coin’s ecosystem.
Let’s break down the key features of a DAO to better understand how they operate:
- Transparency: Since DAOs operate on the blockchain, all transactions (voting, proposals, payments, etc) are stored on the network and can be viewed by the public. Additionally, many DAOs are open source, so users can view the underlying code that runs the project.
- Autonomy: Once DAO smart contracts are live, they continue to operate and execute decisions based on the community’s votes as long as the underlying blockchain is active.
- Decentralization: With no central figure carrying out orders, DAOs will operate based on predefined rules and uphold the majority of token holders’ decisions. The more distributed the governance tokens are, the greater the decentralization.
Why Are DAOs Important in Crypto?
Through tokenized governance, DAOs help promote community and social activity in blockchain projects. As many investors know, strong and sustainable community engagement is key to a cryptocurrency’s long-term success. DAOs can make crypto platforms more trustworthy and transparent, which increases investors’ and community members’ confidence in the project.
By allowing token holders to propose, vote on, and initiate changes, DAOs create a shared system where every stakeholder’s voice contributes to shaping the project’s direction. This democratization of the decision-making process further reinforces some of the core values in blockchain technology: decentralization and transparency.
Beyond governance, DAOs have become catalysts for innovation across finance, art, gaming, and even environmental initiatives. For instance, the eco-friendly crypto VebetterDAO (B3TR) is a DAO platform that empowers its community through incentive distribution, asset management, and a V2E (Vote-to-Earn) protocol, all focused on sustainability.
Categories of DAO Projects
The DAO framework can be applied to many crypto projects, enabling community-driven upgrades, new partnerships, and platform updates. We categorized some of the most common DAO use cases by purpose and impact.
Financial and DeFi DAOs
These decentralized autonomous organizations are central to the DeFi ecosystem, offering open and transparent financial services. Users may be able to vote on new collaborations, token pairs, and other finance-related developments. Examples include:
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Popular decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Sushi Swap are DAO-based crypto platforms. In particular, Uniswap is an excellent example of a successful DAO that recently voted on $165 million in funding to propel its growth.
- Lending and Borrowing Platforms: Aave and Compound are both lending platforms that are also DAOs. In the case of Compound, token holders can vote on features like interest rates, collateral adjustments, and rewards on the decentralized app.
- Yield Farming and Staking: Platforms like Yearn Finance rely on DAOs that allow users to propose and vote to change or add new services, such as supported tokens, vaults, and fee restructuring.
Based on these examples, DAOs demonstrate how finance can function through transparent and community-led initiatives.
Social and Community DAOs
Social and community-focused DAOs are built around shared values and interests, allowing members to collaborate, fund ideas, and shape collective goals.
Creator collectives use the DAO model to support artists, musicians, and independent creators. Mirror DAO is an example of a Web3 publishing DAO that helps artists launch projects, distribute revenue fairly, and remain independent from traditional publishers.
Another social DAO that focuses on personal interests in Friends With Benefits (FWB). According to The New York Times, FWB has nearly 6,000 token holders and is comprised of crypto enthusiasts interested in Web3 ventures. Today, Friends With Benefits is a social network with a decentralized collective fund and decentralized community endeavors.
Infrastructure and Development DAOs
DAOs that help maintain and grow the technical foundations of the blockchain ecosystem drive innovations in funding and open-source projects. Let’s go over some infrastructure and development DAO examples:
- Protocol Development: Maker (MKR) and Polkadot (DOT) utilize decentralized governance to help maintain and upgrade core blockchain protocols. Polkadot’s platform has an active DAO community of 1.3 million members with over 1,000 governance proposals.
- Tooling and Frameworks: Crypto projects like Optimism (OP) use DAO governance to reward developers for building tools, debugging programs, and libraries supporting blockchain builders.
By funding public innovation, these DAOs support growth and development within their respective on-chain ecosystems and the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Metaverse and Gaming DAOs
Since the rise of digital gaming economies and the metaverse, DAOs have been implemented on Web3 gaming projects for player-focused updates and governance. Some examples include:
- Virtual Worlds Governance: Victoria VR and other virtual world projects will implement a DAO to give players and creators control over the gaming platform’s future iterations. Governance token holders can change policies that determine how the VR worlds behave.
- Gaming Guilds: Blockchain platforms like MetaGaming Guild (MGG) have DAOs that help community members pool resources and invite scholars to earn rewards in P2E games that may be redistributed within the platform.
These examples show how decentralized autonomous organizations can empower creators, players, and other community members by directing financial and governance incentives towards a single goal.
What Are the Benefits of DAOs?
DAOs offer several advantages, making them a more suitable alternative to conventional organizational structures, especially when implemented in blockchain projects.
Enhanced Transparency and Trust
With all code executions, transactions, and decisions recorded on the blockchain, DAOs give an unmatched level of transparency that adds to crypto platforms’ trustworthiness. Even non-member users without governance tokens can view proposals and transactions on the decentralized ledger.
At the smart contract level, many DAOs make their source codes available to the public, typically through open-source forums like GitHub. Because smart contracts dictate how DAOs operate, allowing anyone to view the underlying programming adds another layer of transparency for token holders and developers.
Increased Inclusivity and Participation
Most DAOs allow anyone to participate in decentralized governance, as long as they own the necessary governance tokens and can connect to the platform. This makes them far more inclusive than traditional institutions and companies that often employ a screening process that can be influenced by biases and other factors.

Since practically anyone can propose ideas and vote for new developments, DAOs encourage contributions from various perspectives. The larger the DAO project’s community, the more diverse it’s likely to be. Proposals and discussions based on many skill sets and backgrounds can have a synergistic effect for a versatile approach to problem-solving within the platform.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Many crypto projects create DAOs to ensure long-term platform sustainability that can only be achieved with a flexible structure. Cryptocurrencies built to evolve with DAOs can adapt to changing market conditions and challenges that may require immediate action. Unlike centralized organizations, where changes come with unnecessary red tape, DAO proposals are automatically executed through smart contracts once their voting requirements are met.
DAO adaptability is even more crucial in highly innovative and competitive markets, where one new technological development may make other projects irrelevant. Categories like AI coins, gaming crypto, and Layer-2 (L2) projects may implement DAOs for greater flexibility.
How We Chose the DAO Projects
When we evaluated the best DAO crypto projects, we focused on how each platform operates, rewards its members, encourages community involvement, and maintains long-term viability. Let’s break all these down.
Decision-Making Processes
We considered projects with well-defined governance models, prioritizing their long-term goals and community contributions. In particular, platforms with transparent documentation on their official sites showcasing how their voting and proposal systems operate were considered more trustworthy.
Some DAO governance structures implement different voting mechanisms that can affect how the platforms make decisions. For example, VebetterDAO used Quadratic Voting (QV), which reduces the impact of significant token holders when voting. QV promotes a more balanced decision-making process, especially for projects with unequal governance token distribution.
Tokenomics and Incentives
Other key factors in our evaluations include token utility and distribution. We observed additional token functionality besides governance, such as staking, rewards, access to services, etc. Afterward, we analyzed how these utilities complemented the project’s goals and use cases.
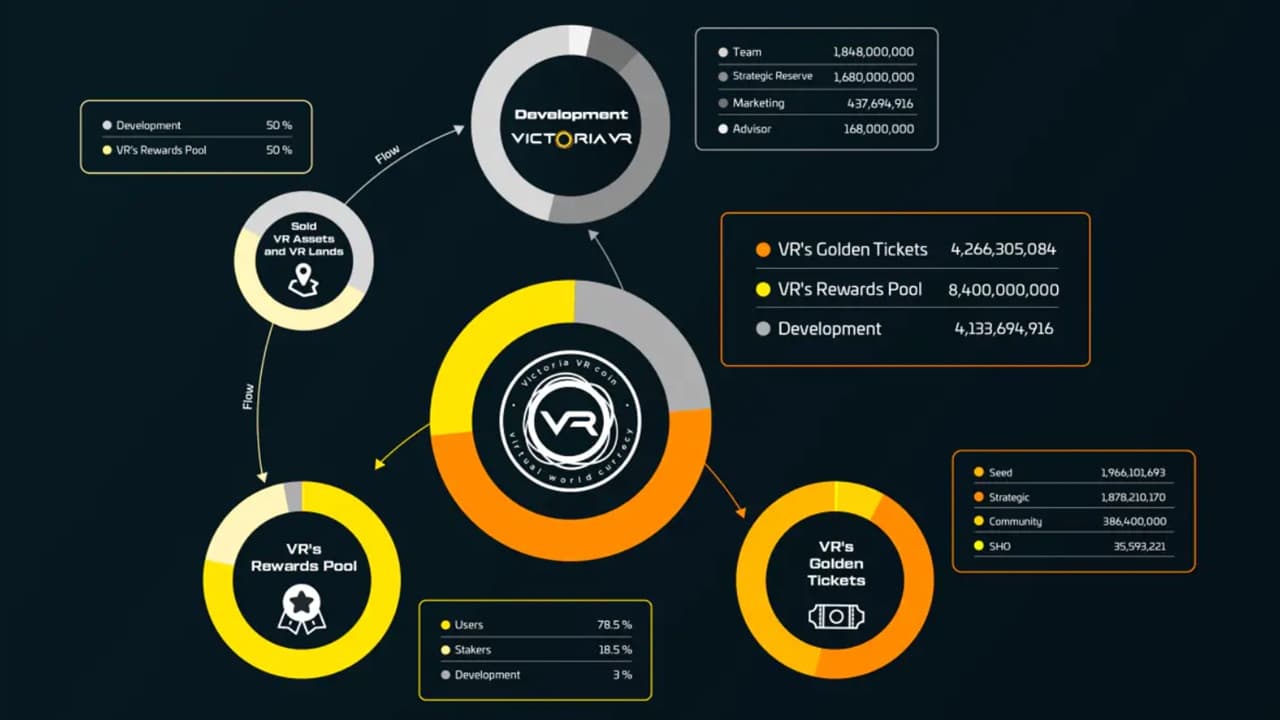
Additionally, we considered token distribution to see how decentralized the DAO projects are. Platforms with one or more majority token holders may be subject to higher centralization risk, which can be exploited in decentralized autonomous organizations.
Active Participation
For crypto projects in general, community engagement reflects how well a project is backed by its token holders and can be a strong indicator of long-term viability. Within the context of DAOs, high community activity means that the project’s ecosystem can be continuously updated with new proposals and discussions that help drive the crypto forward.
Great DAO crypto projects incentivize community participation through active forums, live discussions, and even partnerships with major crypto investors and firms.
Security and Sustainability
Given the high-risk environment in cryptocurrencies, we placed significant importance on each DAO’s smart contract security and treasury structures. We favored projects that underwent third-party audits, have open-source codes, and implement safety mechanisms with signs of high token holder distribution.
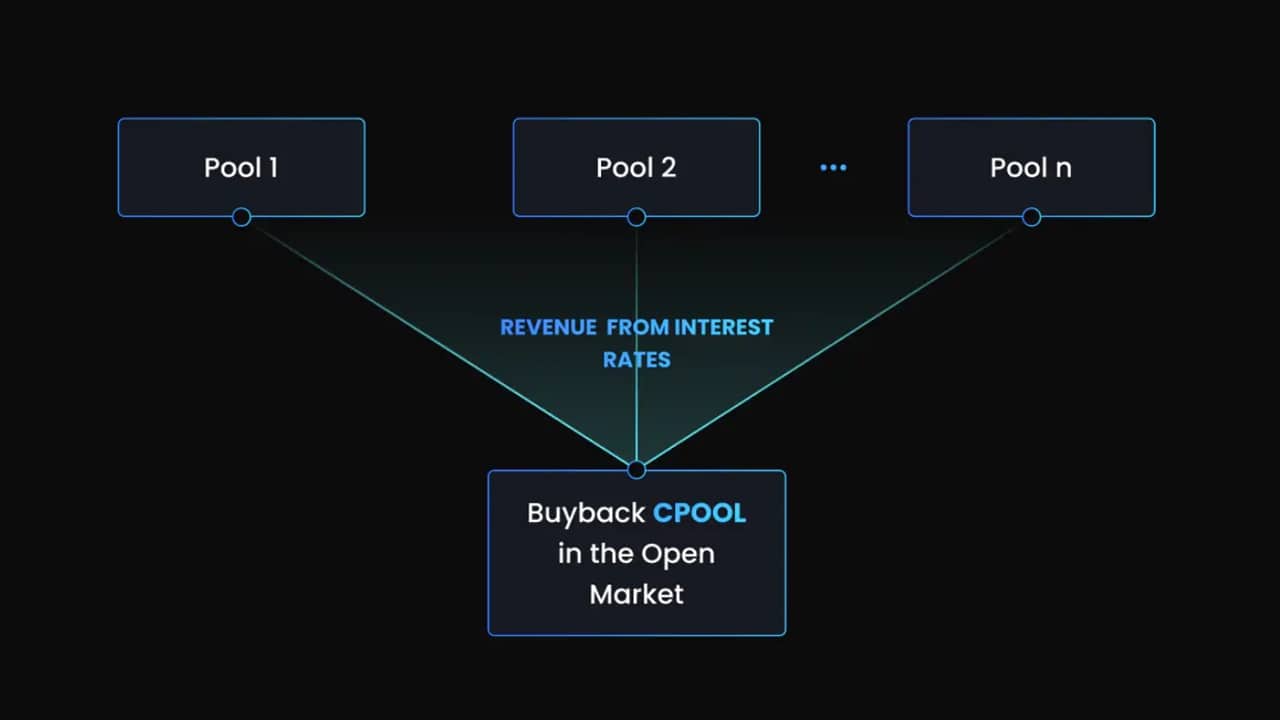
Another considerable factor is project sustainability. This involves identifying how a DAO’s tokenomics can fund itself and the community over time and how rewards and other income-generating activities pave the way for long-term operations.
The Future of DAOs
The next step for decentralized autonomous organizations may not be about turning them into digital replicas of corporations. Instead, it should focus on harnessing their potential as unique, blockchain-oriented platforms. As Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin argued, DAOs serve a broader mission beyond maximizing profit.
If DAOs do not replace conventional institutions, progress will be made towards collaborating with traditional organizations. Partnerships can be structured around shared goals, resource pooling, and co-governance, where decision-making is distributed. This hybrid approach preserves decentralization while allowing for practical coordination, especially on complex or large-scale initiatives.
Legally, DAOs still face regulatory uncertainty. As Buterin notes, DAOs operate more like a sovereign legal entity than a subsidiarie. The challenge is to navigate changing regulations without giving up the decentralized values that make DAOs unique. The current legal ambiguity surrounding DAOs creates both risks and opportunities.
Ultimately, the future of DAOs will be shaped by their ability to maintain their decentralized foundations while adapting to real-world demands. To do this, future DAOs may need to find a compromise between governance hierarchy and a fully democratized decision-making model.
Due to DAOs’ highly sovereign nature, many crypto figureheads like Buterin believe developers and regulators should look towards political science and democratic systems rather than corporate models to unlock DAOs’ full potential.
DAO Projects FAQs
What is the primary purpose of a DAO?
A DAO (decentralized autonomous organization) is designed to let communities make collective decisions and manage shared resources without relying on a central authority. The core goal is to create transparent, smart contract-based governance in the blockchain.
How can one participate in a DAO?
Users can join a DAO by acquiring its governance token, which allows them to vote on project proposals, contribute new ideas, and participate in overall decision-making.
Are DAOs legally recognized entities?
Generally, DAOS are not legally recognized entities. They will persistently operate, so long as the majority of the stakeholders allow it to do so.
What are the risks associated with joining a DAO?
Some risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, lack of legal protection, and market volatility in governance tokens.
Can DAOs generate revenue?
DAOs can earn income in various ways, including investment returns, protocol fees, products and services, and reinvestments into the community.
How do DAOs ensure security and trustworthiness?
DAOs primarily rely on well-built smart contracts to remain secure and usually make their code open source for transparency. Third-party audits, community reviews, and whitepapers can also help build trust.
References
- Jane Street Uses DeFi to Borrow Cryptocurrency – Bloomberg (Bloomberg)
- What are play-to-earn crypto games? | Learn how to earn crypto while gaming (Kraken)
- Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO): Definition, Purpose, and Example (Investopedia)
- Uniswap Passes $165M Funding Plan After DAO Vote (Yahoo Finance)
- Tally | Compound Proposals (Compound)
- Friends With Benefits Social Club Runs On Crypto and Vibes – The New York Times (The New York Times)
- Retro Funding: Dev Tooling – OP Atlas (Optimism)
- DAOs are not corporations: where decentralization in autonomous organizations matters (Vitalik Buterin Website)