On this Page:
The rise of Bitcoin ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, has changed the cryptocurrency market and the financial world at large forever. These game-changing investment vehicles successfully bridged the gap between digital currencies and traditional finance, finally enabling mainstream investors and financial institutions to easily and securely gain exposure to Bitcoin.
Bitcoin ETFs opened the floodgates to institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies by bringing regulatory clarity and increased accessibility to the industry. Bitcoin is no longer sidelined by institutional investors and regulators, and the financial market’s embrace of the technology has helped improve perceptions of the asset.
In this article, we detail everything you need to know about Bitcoin ETFs, from pros and cons to an in-depth exploration of their effects on the crypto market and more.
How Do Bitcoin ETFs Work?
Before we get to Bitcoin ETFs, let’s break down what exactly an ETF or exchange-traded fund is. An ETF is a kind of investment fund that holds any number of assets, such as stocks, commodities, bonds, real estate, and other financial instruments. They are traded on stock exchanges like any other public stock, making it easy for investors to gain exposure to various bundles of assets without having to purchase them and manage them directly.
A Bitcoin ETF is simply an ETF that tracks the price of Bitcoin, allowing investors to easily gain exposure to the token. There are various kinds of Bitcoin ETFs that hold different assets. For example, some only hold Bitcoin while others purchase Bitcoin futures contracts.
A Brief History of Bitcoin ETFs
The first Bitcoin ETF started trading on October 19th, 2021, but the idea has been around for over a decade. In fact, the first serious attempt to launch a Bitcoin ETF came in 2013, just a few years after the token was created. The Winklevoss Twins, famous for their involvement in Facebook and their early Bitcoin investments, filed a proposal for the Winklevoss Bitcoin Trust ETF with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission in 2013.
The SEC didn’t make a decision until 2017 when it denied the application. The SEC was mostly worried about the potential for fraud and cited the minimal regulation in the crypto industry at the time. In the notice, the SEC said:
“As discussed further below, the Commission is disapproving this proposed rule change because it does not find the proposal to be consistent with Section 6(b)(5) of the Exchange Act, which requires, among other things, that the rules of a national securities exchange be designed to prevent fraudulent and manipulative acts and practices and to protect investors and the public interest.”
Supporters of Bitcoin ETFs didn’t give up, and multiple institutions submitted their own proposals. In 2017, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) decided to offer trading of Bitcoin futures contracts, marking a shift towards institutional adoption.
ProShares, a large ETF issuer, proposed a Bitcoin ETF that only holds Bitcoin futures, providing exposure to the token without owning it directly. After many delays, the SEC finally approved the ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF in October 2021. It took another few years for the SEC to approve the first spot Bitcoin ETFs, which directly hold Bitcoin.
In the short time that Bitcoin ETFs have been around, they have already had a massive impact on the crypto market, spurring billions of dollars of inflows from institutions and traditional investors.
Investing in Bitcoin vs Bitcoin ETFs
It may seem like investing in Bitcoin versus Bitcoin ETFs is virtually identical, and in many ways, they are, but there are crucial differences to keep in mind. The biggest difference, for the most part, is how you invest in each asset.
When you want to directly purchase Bitcoin, you have to go through the trouble of setting up an account with a cryptocurrency exchange, such as Coinbase or Kraken. From there, you need to verify your identity with a driver’s license (or other form of valid ID) and personal information. Finally, you can deposit funds and start trading Bitcoin.
On the other hand, investing in Bitcoin ETFs requires a brokerage account (with similar verification requirements). If you already have one set up, you can go ahead and use it to trade Bitcoin ETFs to your heart’s desire.
Directly owning Bitcoin also requires you to store it securely. Many investors simply leave their cryptocurrencies in their exchange accounts, but this is generally frowned upon by security experts as it incurs a significant counterparty risk.
Most experts advise investors to make their own secure personal wallet, ideally a hardware wallet, to hold their tokens safely. Unlike with Bitcoin ETFs, investors can easily transfer and use their Bitcoin in various ways. For example, Bitcoin can be deposited and used in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to earn interest, borrow, and swap for other tokens.
ETF fees are another factor to consider when deciding between Bitcoin and Bitcoin ETFs. Crypto exchanges charge trading fees (and sometimes small wallet transfer costs), but they rarely charge any ongoing management fees. Bitcoin ETFs, like all other kinds of ETFs, often charge both ongoing management and expense fees, eroding your holdings over time (though they are usually relatively small).
Finally, the regulatory status of Bitcoin ETFs can provide greater confidence and safety to investors because they are subject to stricter financial regulations and protections than Bitcoin.
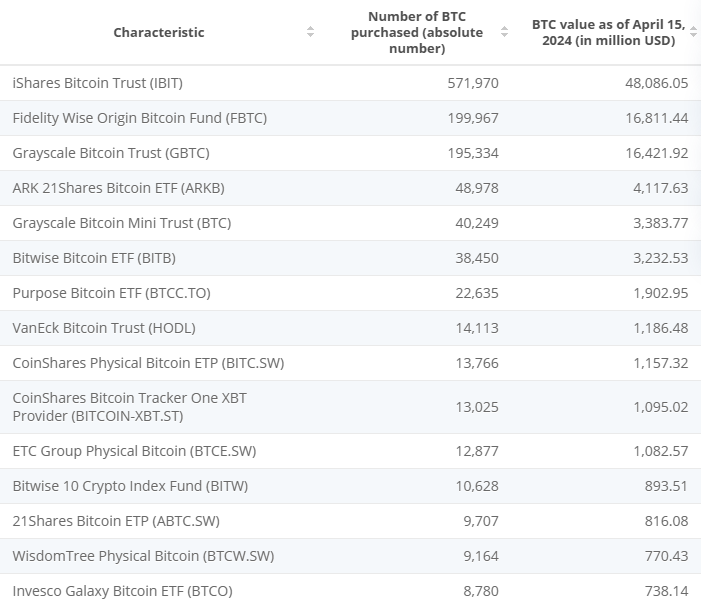
10 Largest Bitcoin ETFs (& ETP)
Here are the largest Bitcoin ETFs in the world:
- iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.25% fees
- Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund (FBTC)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.25% fees
- Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 1.5% fees (significantly higher than competitors)
- ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (ARKB)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.21% fees
- Grayscale Bitcoin Mini Trust (BTC)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.15% fees (lowest fees of any BTC ETF)
- Bitwise Bitcoin ETF (BITB)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.2% fees
- Purpose Bitcoin ETF (BTCC.TO)
- Canadian spot Bitcoin ETF with 1.49% fees
- VanEck Bitcoin Trust (HODL)
- Spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.2% fees
- CoinShares Physical Bitcoin ETP (BITC.SW)
- European spot Bitcoin ETF with 0.25% fees
- CoinShares Bitcoin Tracker One XBT Provider (BITCOIN-XBT.ST)
- European Bitcoin exchange-traded product (ETP), physically holds Bitcoin
Other Crypto ETFs
As Bitcoin ETFs have become more and more popular, similar ETFs focused on other cryptocurrencies, mostly Ethereum, are following closely behind. Like Bitcoin ETFs, they provide easy and regulated access to exposure to these assets, without all of the trouble of using crypto exchanges.
Ethereum ETFs
Ethereum ETFs track the price of Ethereum and come in two main types: spot ETFs, which directly hold Ethereum, and futures ETFs, which hold Ethereum futures contracts. Some of the most popular Ethereum ETFs include Valkyrie Ethereum Strategy ETF ($BTF), ProShares Ether Strategy ETF ($EETH), and Grayscale Ethereum Trust ($ETHE). $EETH and $BTF are both futures-based ETFs, while Grayscale’s $ETHE holds Ethereum directly.
Multi-Asset Crypto ETFs
One of the newest and most exciting kinds of crypto ETFs are multi-asset crypto ETFs. ProShares’ Bitcoin & Ether Equal Weight Strategy ETF ($BETE) is a popular example that provides exposure to both Bitcoin and Ethereum, holding futures contracts.
ETF issuers have also launched specialized ETFs that focus on crypto stocks rather than cryptocurrencies themselves. For example, Bitwise offers its Crypto Industry Innovators ETF ($BITQ), which gives exposure to various important crypto infrastructure stocks.
How Bitcoin ETFs Changed the Crypto Market
For years, Bitcoin ETFs were hailed as the next frontier of the cryptocurrency market, with hopes of unlocking billions of dollars of institutional investment. It turned out that analysts were at least partially correct, with institutional inflows surging to all-time highs.
Bitcoin ETFs are also simply a great tool for investors of all kinds, from retail investors with a few hundred dollars to spend to hedge funds with millions or billions of dollars under management. They allow investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin quickly, securely, and easily without having to make an account with a crypto exchange.
While Bitcoin ETFs aren’t the perfect solution to all of crypto’s problems, they have undeniably brought legitimacy and regulatory clarity to the market. As the institutional community continues to adapt to the new order of digital assets, crypto ETFs will likely continue to play an important role, offering a middle-ground between the decentralized ideals of crypto and the centralized world of traditional finance.
FAQs
What's the difference between buying Bitcoin and investing in a Bitcoin ETF?
Purchasing Bitcoin gives you direct ownership over the token while investing in a Bitcoin ETF allows you to gain exposure to the price of Bitcoin in a regulated environment without managing it yourself.
How do Bitcoin ETFs work?
Bitcoin ETFs are simply publicly traded funds that own Bitcoin or Bitcoin futures to track the price of Bitcoin.
Can I invest in Bitcoin ETFs with my retirement account?
Yes. You can invest in most Bitcoin ETFs through IRA accounts, though you may be restricted from investing in ETFs that aren't listed on U.S. exchanges (such as the Purpose Bitcoin ETF, listed in Canada).

